Page 230 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 230
Free Radical Chain Polymerization 193
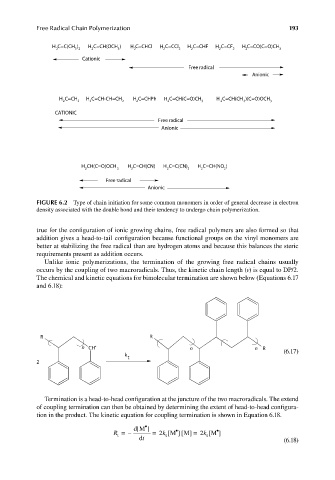
H C=C(CH ) H C=CH(OCH ) H C=CHCl H C=CCl H C=CHF H C=CF H C=CO(C=O)CH
2 3 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3
Cationic
Free radical
Anionic
H C=CH H C=CH-CH=CH H C=CHPh H C=CH(C=O)CH H C=CH(CH )(C=O)OCH
2 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 3 3
CATIONIC
Free radical
Anionic
H CH(C=O)OCH H C=CH(CN) H C=C(CN) H C=CH(NO )
2 3 2 2 2 2 2
Free radical
Anionic
FIGURE 6.2 Type of chain initiation for some common monomers in order of general decrease in electron
density associated with the double bond and their tendency to undergo chain polymerization.
true for the configuration of ionic growing chains, free radical polymers are also formed so that
addition gives a head-to-tail configuration because functional groups on the vinyl monomers are
better at stabilizing the free radical than are hydrogen atoms and because this balances the steric
requirements present as addition occurs.
Unlike ionic polymerizations, the termination of the growing free radical chains usually
occurs by the coupling of two macroradicals. Thus, the kinetic chain length (v) is equal to DP/2.
The chemical and kinetic equations for bimolecular termination are shown below (Equations 6.17
and 6.18):
R R
n CH • n n R
k (6.17)
t
2
Termination is a head-to-head configuration at the juncture of the two macroradicals. The extend
of coupling termination can then be obtained by determining the extent of head-to-head confi gura-
tion in the product. The kinetic equation for coupling termination is shown in Equation 6.18.
•
d[M ] • •
R t =− = 2 [M ] [M]k t = 2 [M ]k t
dt (6.18)
9/14/2010 3:39:25 PM
K10478.indb 193 9/14/2010 3:39:25 PM
K10478.indb 193