Page 370 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 370
Naturally Occurring Polymers—Animals 333
Disulfide bonds
Hydrophobic/Aromatic
NH
H
S NH +
3
O-H
S –
COO
Hydrogen bonding
Ionic bond/Salt bridge
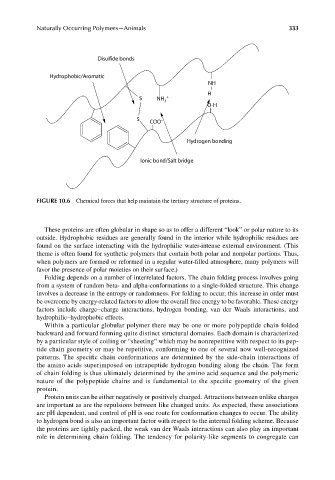
FIGURE 10.6 Chemical forces that help maintain the tertiary structure of proteins.
These proteins are often globular in shape so as to offer a different “look” or polar nature to its
outside. Hydrophobic residues are generally found in the interior while hydrophilic residues are
found on the surface interacting with the hydrophilic water-intense external environment. (This
theme is often found for synthetic polymers that contain both polar and nonpolar portions. Thus,
when polymers are formed or reformed in a regular water-filled atmosphere, many polymers will
favor the presence of polar moieties on their surface.)
Folding depends on a number of interrelated factors. The chain folding process involves going
from a system of random beta- and alpha-conformations to a single-folded structure. This change
involves a decrease in the entropy or randomness. For folding to occur, this increase in order must
be overcome by energy-related factors to allow the overall free energy to be favorable. These energy
factors include charge–charge interactions, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals interactions, and
hydrophilic–hydrophobic effects.
Within a particular globular polymer there may be one or more polypeptide chain folded
backward and forward forming quite distinct structural domains. Each domain is characterized
by a particular style of coiling or “sheeting” which may be nonrepetitive with respect to its pep-
tide chain geometry or may be repetitive, conforming to one of several now well-recognized
patterns. The specific chain conformations are determined by the side-chain interactions of
the amino acids superimposed on intrapeptide hydrogen bonding along the chain. The form
of chain folding is thus ultimately determined by the amino acid sequence and the polymeric
nature of the polypeptide chains and is fundamental to the specific geometry of the given
protein.
Protein units can be either negatively or positively charged. Attractions between unlike charges
are important as are the repulsions between like changed units. As expected, these associations
are pH dependent, and control of pH is one route for conformation changes to occur. The ability
to hydrogen bond is also an important factor with respect to the internal folding scheme. Because
the proteins are tightly packed, the weak van der Waals interactions can also play an important
role in determining chain folding. The tendency for polarity-like segments to congregate can
9/14/2010 3:41:12 PM
K10478.indb 333 9/14/2010 3:41:12 PM
K10478.indb 333