Page 606 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 606
Synthesis of Reactants and Intermediates for Polymers 569
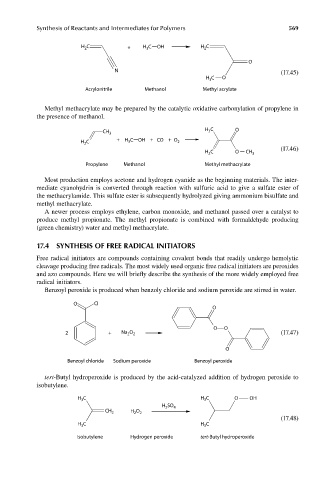
H 2 C + H C OH H 2 C
3
O
N (17.45)
H C O
3
Acrylonitrile Methanol Methyl acrylate
Methyl methacrylate may be prepared by the catalytic oxidative carbonylation of propylene in
the presence of methanol.
H C O
CH 3 3
H C + H C OH + CO + O 2
3
2
(17.46)
C O
H 2 CH 3
Propylene Methanol Methyl methacrylate
Most production employs acetone and hydrogen cyanide as the beginning materials. The inter-
mediate cyanohydrin is converted through reaction with sulfuric acid to give a sulfate ester of
the methacrylamide. This sulfate ester is subsequently hydrolyzed giving ammonium bisulfate and
methyl methacrylate.
A newer process employs ethylene, carbon monoxide, and methanol passed over a catalyst to
produce methyl propionate. The methyl propionate is combined with formaldehyde producing
(green chemistry) water and methyl methacrylate.
17.4 SYNTHESIS OF FREE RADICAL INITIATORS
Free radical initiators are compounds containing covalent bonds that readily undergo hemolytic
cleavage producing free radicals. The most widely used organic free radical initiators are peroxides
and azo compounds. Here we will briefl y describe the synthesis of the more widely employed free
radical initiators.
Benzoyl peroxide is produced when benzoly chloride and sodium peroxide are stirred in water.
O Cl
O
O O
2 + Na O (17.47)
2 2
O
Benzoyl chloride Sodium peroxide Benzoyl peroxide
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide is produced by the acid-catalyzed addition of hydrogen peroxide to
isobutylene.
H C H 3 C O OH
3
H SO 4
2
CH 2 H 2 O 2
(17.48)
H C H C
3
3
Isobutylene Hydrogen peroxide tert-Butyl hydroperoxide
9/14/2010 3:43:31 PM
K10478.indb 569 9/14/2010 3:43:31 PM
K10478.indb 569