Page 67 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 67
30 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
Eclipsed
H H
H
H
H
H
Energy
12 kJ/mol
H H H H
H H H H
H H H H
Staggered Staggered
Rotation
CH 3 H CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 H
H
H H H CH 3 H
H CH 3 H H H H
Anti Eclipsed Gauche
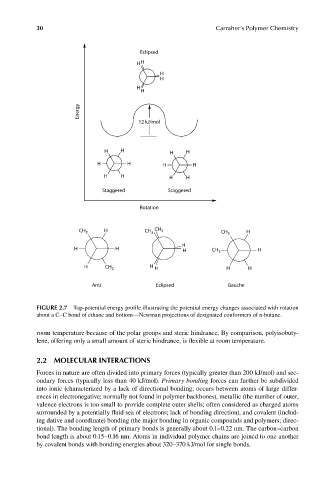
FIGURE 2.7 Top-potential energy profile illustrating the potential energy changes associated with rotation
about a C–C bond of ethane and bottom—Newman projections of designated conformers of n-butane.
room temperature because of the polar groups and steric hindrance. By comparison, polyisobuty-
lene, offering only a small amount of steric hindrance, is flexible at room temperature.
2.2 MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS
Forces in nature are often divided into primary forces (typically greater than 200 kJ/mol) and sec-
ondary forces (typically less than 40 kJ/mol). Primary bonding forces can further be subdivided
into ionic (characterized by a lack of directional bonding; occurs between atoms of large differ-
ences in electronegative; normally not found in polymer backbones), metallic (the number of outer,
valence electrons is too small to provide complete outer shells; often considered as charged atoms
surrounded by a potentially fluid sea of electrons; lack of bonding direction), and covalent (includ-
ing dative and coordinate) bonding (the major bonding in organic compounds and polymers; direc-
tional). The bonding length of primary bonds is generally about 0.1–0.22 nm. The carbon–carbon
bond length is about 0.15–0.16 nm. Atoms in individual polymer chains are joined to one another
by covalent bonds with bonding energies about 320–370 kJ/mol for single bonds.
9/14/2010 3:35:56 PM
K10478.indb 30
K10478.indb 30 9/14/2010 3:35:56 PM