Page 86 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 86
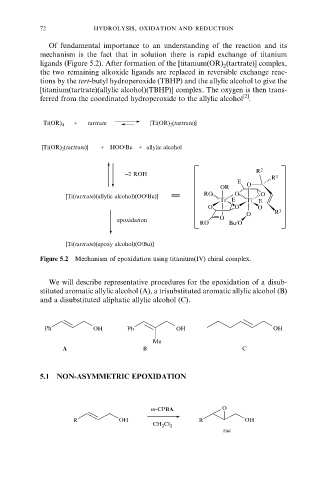
72 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
Of fundamental importance to an understanding of the reaction and its
mechanism is the fact that in solution there is rapid exchange of titanium
ligands (Figure 5.2). After formation of the [titanium(OR) (tartrate)] complex,
2
the two remaining alkoxide ligands are replaced in reversible exchange reac-
tions by the tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) and the allylic alcohol to give the
[titanium(tartrate)(allylic alcohol)(TBHP)] complex. The oxygen is then trans-
[2]
ferred from the coordinated hydroperoxide to the allylic alcohol .
Ti(OR) + tartrate [Ti(OR) (tartrate)]
2
4
t
[Ti(OR) (tartrate)] + HOO Bu + allylic alcohol
2
R 2
−2 ROH R 1
E
OR O
t
[Ti(tartrate)(allylic alcohol)(OO Bu)] RO O O
Ti E Ti E
O O O
O R 3
epoxidation O
t
RO Bu O
t
[Ti(tartrate)(epoxy alcohol)(O Bu)]
Figure 5.2 Mechanism of epoxidation using titanium(IV) chiral complex.
We will describe representative procedures for the epoxidation of a disub-
stituted aromatic allylic alcohol (A), a trisubstituted aromatic allylic alcohol (B)
and a disubstituted aliphatic allylic alcohol (C).
Ph OH Ph OH OH
Me
A B C
5.1 NON-ASYMMETRIC EPOXIDATION
m-CPBA O
R OH R OH
CH 2 Cl 2
rac