Page 114 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 114
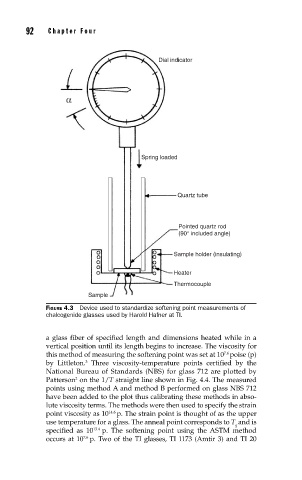
92 Cha pte r F o u r
Dial indicator
α
Spring loaded
Quartz tube
Pointed quartz rod
(90° included angle)
Sample holder (insulating)
Heater
Thermocouple
Sample
FIGURE 4.3 Device used to standardize softening point measurements of
chalcogenide glasses used by Harold Hafner at TI.
a glass fiber of specified length and dimensions heated while in a
vertical position until its length begins to increase. The viscosity for
this method of measuring the softening point was set at 10 poise (p)
7.6
3
by Littleton. Three viscosity-temperature points certified by the
National Bureau of Standards (NBS) for glass 712 are plotted by
2
Patterson on the 1/T straight line shown in Fig. 4.4. The measured
points using method A and method B performed on glass NBS 712
have been added to the plot thus calibrating these methods in abso-
lute viscosity terms. The methods were then used to specify the strain
point viscosity as 10 14.6 p. The strain point is thought of as the upper
use temperature for a glass. The anneal point corresponds to T and is
g
specified as 10 13.4 p. The softening point using the ASTM method
occurs at 10 p. Two of the TI glasses, TI 1173 (Amtir 3) and TI 20
7.6