Page 128 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 128
Characterization of Glass Pr operties 105
Digital Par phase sensitive
voltmeter amplifier
Stepping motor
655, 360 steps/360°
Hg Cd Te
detector
Eason computer
control 1 step = 2
arc seconds
Optical 100
cycle
chopper
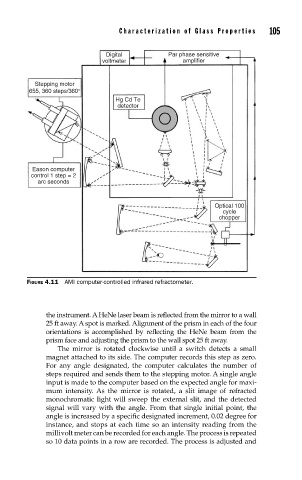
FIGURE 4.11 AMI computer-controlled infrared refractometer.
the instrument. A HeNe laser beam is reflected from the mirror to a wall
25 ft away. A spot is marked. Alignment of the prism in each of the four
orientations is accomplished by reflecting the HeNe beam from the
prism face and adjusting the prism to the wall spot 25 ft away.
The mirror is rotated clockwise until a switch detects a small
magnet attached to its side. The computer records this step as zero.
For any angle designated, the computer calculates the number of
steps required and sends them to the stepping motor. A single angle
input is made to the computer based on the expected angle for maxi-
mum intensity. As the mirror is rotated, a slit image of refracted
monochromatic light will sweep the external slit, and the detected
signal will vary with the angle. From that single initial point, the
angle is increased by a specific designated increment, 0.02 degree for
instance, and stops at each time so an intensity reading from the
millivolt meter can be recorded for each angle. The process is repeated
so 10 data points in a row are recorded. The process is adjusted and