Page 127 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 127
104 Cha pte r F o u r
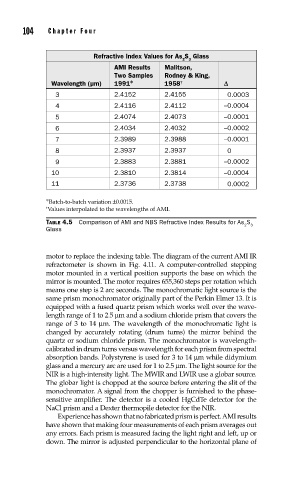
Refractive Index Values for As S Glass
2 3
AMI Results Malitson,
Two Samples Rodney & King,
Wavelength (µm) 1991 * 1958 † D
3 2.4152 2.4155 0.0003
4 2.4116 2.4112 –0.0004
5 2.4074 2.4073 –0.0001
6 2.4034 2.4032 –0.0002
7 2.3989 2.3988 –0.0001
8 2.3937 2.3937 0
9 2.3883 2.3881 –0.0002
10 2.3810 2.3814 –0.0004
11 2.3736 2.3738 0.0002
∗ Batch-to-batch variation ±0.0015.
† Values interpolated to the wavelengths of AMI.
TABLE 4.5 Comparison of AMI and NBS Refractive Index Results for As S
2 3
Glass
motor to replace the indexing table. The diagram of the current AMI IR
refractometer is shown in Fig. 4.11. A computer-controlled stepping
motor mounted in a vertical position supports the base on which the
mirror is mounted. The motor requires 655,360 steps per rotation which
means one step is 2 arc seconds. The monochromatic light source is the
same prism monochromator originally part of the Perkin Elmer 13. It is
equipped with a fused quartz prism which works well over the wave-
length range of 1 to 2.5 µm and a sodium chloride prism that covers the
range of 3 to 14 µm. The wavelength of the monochromatic light is
changed by accurately rotating (drum turns) the mirror behind the
quartz or sodium chloride prism. The monochromator is wavelength-
calibrated in drum turns versus wavelength for each prism from spectral
absorption bands. Polystyrene is used for 3 to 14 µm while didymium
glass and a mercury arc are used for 1 to 2.5 µm. The light source for the
NIR is a high-intensity light. The MWIR and LWIR use a globar source.
The globar light is chopped at the source before entering the slit of the
monochromator. A signal from the chopper is furnished to the phase-
sensitive amplifier. The detector is a cooled HgCdTe detector for the
NaCl prism and a Dexter thermopile detector for the NIR.
Experience has shown that no fabricated prism is perfect. AMI results
have shown that making four measurements of each prism averages out
any errors. Each prism is measured facing the light right and left, up or
down. The mirror is adjusted perpendicular to the horizontal plane of