Page 123 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 123
100 Cha pte r F o u r
M 2
Thermocouple leads
PE 301
To pump
Heat shield
∗
M 4
M 1
Optical wedge
NaCl plates
1st slit
∗ Sample dewar
30 seconds of
ARC indexing table M 5
2nd slit
Thermocouple detector
M 6
M 3
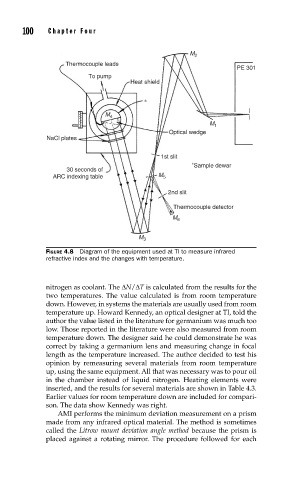
FIGURE 4.8 Diagram of the equipment used at TI to measure infrared
refractive index and the changes with temperature.
nitrogen as coolant. The ∆N/∆T is calculated from the results for the
two temperatures. The value calculated is from room temperature
down. However, in systems the materials are usually used from room
temperature up. Howard Kennedy, an optical designer at TI, told the
author the value listed in the literature for germanium was much too
low. Those reported in the literature were also measured from room
temperature down. The designer said he could demonstrate he was
correct by taking a germanium lens and measuring change in focal
length as the temperature increased. The author decided to test his
opinion by remeasuring several materials from room temperature
up, using the same equipment. All that was necessary was to pour oil
in the chamber instead of liquid nitrogen. Heating elements were
inserted, and the results for several materials are shown in Table 4.3.
Earlier values for room temperature down are included for compari-
son. The data show Kennedy was right.
AMI performs the minimum deviation measurement on a prism
made from any infrared optical material. The method is sometimes
called the Litrow mount deviation angle method because the prism is
placed against a rotating mirror. The procedure followed for each