Page 122 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 122
Characterization of Glass Pr operties 99
1.0 µm 1.25 µm 1.5 µm 1.75 µm 2.0 µm
70 70
0.9 µm
0.8 µm 60
50 50
40 40
30 30
20 20
10 10
Amtir 4 absorption edge transmission
(2.6 cm thickness)
0 0
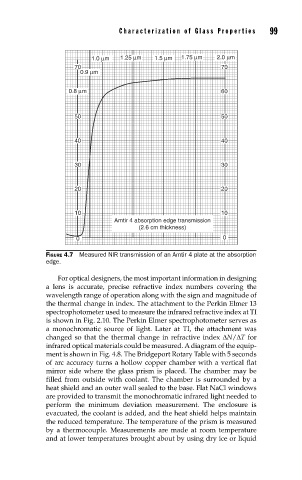
FIGURE 4.7 Measured NIR transmission of an Amtir 4 plate at the absorption
edge.
For optical designers, the most important information in designing
a lens is accurate, precise refractive index numbers covering the
wavelength range of operation along with the sign and magnitude of
the thermal change in index. The attachment to the Perkin Elmer 13
spectrophotometer used to measure the infrared refractive index at TI
is shown in Fig. 2.10. The Perkin Elmer spectrophotometer serves as
a monochromatic source of light. Later at TI, the attachment was
changed so that the thermal change in refractive index ∆N/∆T for
infrared optical materials could be measured. A diagram of the equip-
ment is shown in Fig. 4.8. The Bridgeport Rotary Table with 5 seconds
of arc accuracy turns a hollow copper chamber with a vertical flat
mirror side where the glass prism is placed. The chamber may be
filled from outside with coolant. The chamber is surrounded by a
heat shield and an outer wall sealed to the base. Flat NaCl windows
are provided to transmit the monochromatic infrared light needed to
perform the minimum deviation measurement. The enclosure is
evacuated, the coolant is added, and the heat shield helps maintain
the reduced temperature. The temperature of the prism is measured
by a thermocouple. Measurements are made at room temperature
and at lower temperatures brought about by using dry ice or liquid