Page 189 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 189
Glass Pr ocesses for Other Applications 165
measured again at AMI from room temperature up, it yielded the
same value but with an opposite sign.
Many of the measurements of IR fibers regarding acceptance angle
or attenuation when fibers are bent were made using laser light. Laser
light is very unusual in that it is extremely well collimated, intense,
monochromatic, and to some degree polarized. If the wavelength cor-
responds to an absorption in the glass or clad glass, the results may
be misleading.
The transmission of natural light from a heated source containing
all wavelengths can better be used to characterize infrared fiber for
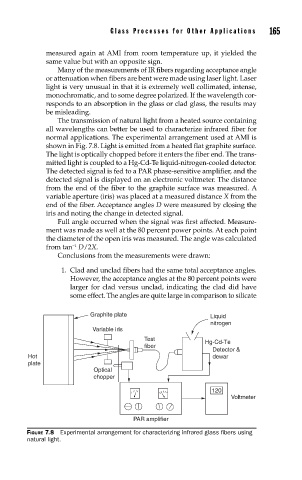
normal applications. The experimental arrangement used at AMI is
shown in Fig. 7.8. Light is emitted from a heated flat graphite surface.
The light is optically chopped before it enters the fiber end. The trans-
mitted light is coupled to a Hg-Cd-Te liquid-nitrogen-cooled detector.
The detected signal is fed to a PAR phase-sensitive amplifier, and the
detected signal is displayed on an electronic voltmeter. The distance
from the end of the fiber to the graphite surface was measured. A
variable aperture (iris) was placed at a measured distance X from the
end of the fiber. Acceptance angles D were measured by closing the
iris and noting the change in detected signal.
Full angle occurred when the signal was first affected. Measure-
ment was made as well at the 80 percent power points. At each point
the diameter of the open iris was measured. The angle was calculated
−1
from tan D/2X.
Conclusions from the measurements were drawn:
1. Clad and unclad fibers had the same total acceptance angles.
However, the acceptance angles at the 80 percent points were
larger for clad versus unclad, indicating the clad did have
some effect. The angles are quite large in comparison to silicate
Graphite plate Liquid
nitrogen
Variable iris
Test
Hg-Cd-Te
fiber
Detector &
Hot dewar
plate
Optical
chopper
120
Voltmeter
PAR amplifier
FIGURE 7.8 Experimental arrangement for characterizing infrared glass fi bers using
natural light.