Page 60 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 60
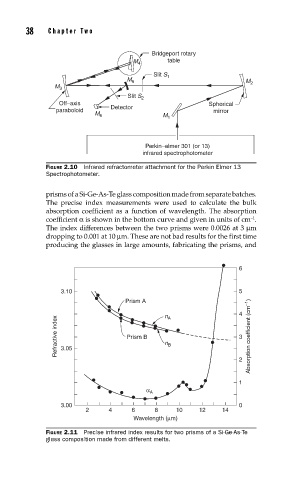
38 Cha pte r T w o
Bridgeport rotary
table
M 4
Slit S 1
M 5
M 2
M 3
Slit S 2
Off–axis Spherical
paraboloid Detector mirror
M 6
M 1
Perkin–elmer 301 (or 13)
infrared spectrophotometer
FIGURE 2.10 Infrared refractometer attachment for the Perkin Elmer 13
Spectrophotometer.
prisms of a Si-Ge-As-Te glass composition made from separate batches.
The precise index measurements were used to calculate the bulk
absorption coefficient as a function of wavelength. The absorption
–1
coefficient α is shown in the bottom curve and given in units of cm .
The index differences between the two prisms were 0.0026 at 3 µm
dropping to 0.001 at 10 µm. These are not bad results for the first time
producing the glasses in large amounts, fabricating the prisms, and
6
3.10 5
Prism A
4
Refractive index Prism B n B 3 Absorption coefficient (cm –1 )
n A
3.05
2
1
α A
3.00 0
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Wavelength (µm)
FIGURE 2.11 Precise infrared index results for two prisms of a Si-Ge-As-Te
glass composition made from different melts.