Page 65 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 65
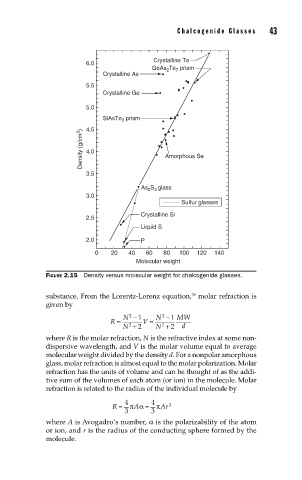
Chalcogenide Glasses 43
Crystalline Te
6.0
GeAs Te 7 prism
2
Crystalline As
5.5
Crystalline Ge
5.0
SiAsTe prism
2
4.5
Density (g/cm 3 ) 4.0 Amorphous Se
3.5
As S 3 glass
2
3.0
Sulfur glasses
Crystalline Si
2.5
Liquid S
2.0 P
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Molecular weight
FIGURE 2.15 Density versus molecular weight for chalcogenide glasses.
35
substance. From the Lorentz-Lorenz equation, molar refraction is
given by
2
2
R = N −1 V = N −1 MW
2
2
N + 2 N + 2 d
where R is the molar refraction, N is the refractive index at some non-
dispersive wavelength, and V is the molar volume equal to average
molecular weight divided by the density d. For a nonpolar amorphous
glass, molar refraction is almost equal to the molar polarization. Molar
refraction has the units of volume and can be thought of as the addi-
tive sum of the volumes of each atom (or ion) in the molecule. Molar
refraction is related to the radius of the individual molecule by
R = 4 πα 4 π Ar
A =
3
3 3
where A is Avogadro’s number, α is the polarizability of the atom
or ion, and r is the radius of the conducting sphere formed by the
molecule.