Page 33 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 33
10 INTRODUCTION
EXAMPLE l.%(continued)
Superheater Rows in line and spaced on 3-in. centers
12 rows of 21411. OD tubes (0.165-in. thick), 47 tubes per row spaced on 3-in. centers
17.44 ft long S = 2460 sqft
Rows in line and spaced on 3t-in. centers A, = 42 sqft
23 tubes per row spaced on 6-in. centers Air heater
S = 3150 sqft 53 rows of 2-in. OD tubes (0.083-in. thick),
A, = 133 sqft approx 13 ft long
Boiler Rows in line and spaced on 2i-in. centers
25 rows of 244x1. OD tubes, approx 18 ft long 41 tubes per row spaced on 3i-in. centers
Rows in line and spaced on 3a-in. centers S = 14,800 sqft
35 tubes per row spaced on 4-in. centers A, (total internal cross section area of 2173 tubes)
S = 10,300 sqft = 39.3 sqft
A, = 85.0 sqft A, (clear area between tubes for crossflow of air)
Economizer = 70 sqft
10 rows of 2-in. OD tubes (0.148-in. thick), Air temperature entering air heater = 80°F
approx 10 ft long
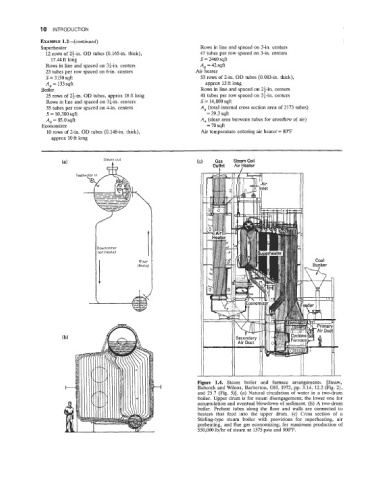
Steam out
(a) Gas Steam Coil
('' Outlet Air Heater
Coa I
fl
Figure 1.4. Steam boiler and furnace arrangements. [Steam,
Babcock and Wilcox, Barberton, OH, 1972, pp. 3.14, 12.2 (Fig. 2),
and 25.7 (Fig. 5)]. (a) Natural circulation of water in a two-drum
boiler. Upper drum is for steam disengagement; the lower one for
accumulation and eventual blowdown of sediment. (b) A two-drum
boiler. Preheat tubes along the floor and walls are connected to
heaters that feed into the upper drum. (c) Cross section of a
Stirling-type steam boiler with provisions for superheating, air
preheating, and flue gas economizing; for maximum production of
550,000 lb/hr of steam at 1575 psia and 900°F.