Page 35 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 35
12 INTRODUCTION
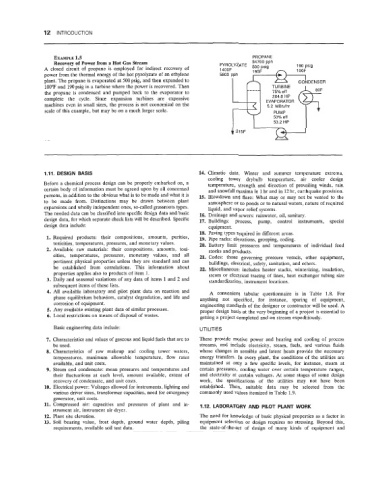
1.5
EXAMPLE PROPANE
34700 pph
Recovery of Power from a Hot Gas Stream PYROLYZATE 500 psig 190 psig
A closed circuit of propane is employed for indirect recovery of 1400F 195F 1 OOF
power from the thermal energy of the hot pyrolyzate of an ethylene 5800 pph I I
plant. The propane is evaporated at 500 psig, and then expanded to CO~JDENSER
100°F and 190 psig in a turbine where the power is recovered. Then
the propane is condensed and pumped back to the evaporator to
204.6 HP
complete the cycle. Since expansion turbines are expensive EVAPORATOR
machines even in small sizes, the process is not economical on the 5.2 MBtUhr
scale of this example, but may be on a much larger scale.
50% eff
1.11. DESIGN BASIS 14. Climatic data. Winter and summer temperature extrema,
cooling tower drybulb temperature, air cooler design
Before a chemical process design can be properly embarked on, a temperature, strength and direction of prevailing winds, rain
certain body of information must be agreed upon by all concerned and snowfall maxima in 1 hr and in 12 hr, earthquake provision.
persons, in addition to the obvious what is to be made and what it is 15. Blowdown and flare: What may or may not be vented to the
to be made from. Distinctions may be drawn between plant atmosphere or to ponds or to natural waters, nature of required
expansions and wholly independent ones, so-called grassroots types. liquid, and vapor relief systems.
The needed data can be classified into specific design data and basic 16. Drainage and sewers: rainwater, oil, sanitary.
design data, for which separate check lists will be described. Specific 17. Buildings: process, pump, control instruments, special
design data include: equipment.
18. Paving types required in different areas.
1. Required products: their compositions, amounts, purities, 19. Pipe racks: elevations, grouping, coding.
toxicities, temperatures, pressures, and monetary values. 20. Battery limit pressures and temperatures of individual feed
2. Available raw materials: their compositions, amounts, toxi- stocks and products.
cities, temperatures, pressures, monetary values, and all 21. Codes: those governing pressure vessels, other equipment,
pertinent physical properties unless they are standard and can buildings, electrical, safety, sanitation, and others.
be established from correlations. This information about 22. Miscellaneous: includes heater stacks, winterizing, insulation,
properties applies also to products of item 1. steam or electrical tracing of lines, heat exchanger tubing size
3. Daily and seasonal variations of any data of items 1 and 2 and standardization, instrument locations.
subsequent items of these lists.
4. All available laboratory and pilot plant data on reaction and A convenient tabular questionnaire is in Table 1.8. For
phase equilibrium behaviors, catalyst degradation, and life and anything not specified, for instance, sparing of equipment,
corrosion of equipment. engineering standards of the designer or constructor will be used. A
5. Any available existing plant data of similar processes. proper design basis at the very beginning of a project is essential to
6. Local restrictions on means of disposal of wastes. getting a project completed and on stream expeditiously.
Basic engineering data include: UTI LlTlES
7. Characteristics and values of gaseous and liquid fuels that are to These provide motive power and heating and cooling of process
be used. streams, and include electricity, steam, fuels, and various fluids
8. Characteristics of raw makeup and cooling tower waters, whose changes in sensible and latent heats provide the necessary
temperatures, maximum allowable temperature, flow rates energy transfers. In every plant, the conditions of the utilities are
available, and unit costs. maintained at only a few specific levels, for instance, steam at
9. Steam and condensate: mean pressures and temperatures and certain pressures, cooling water over certain temperature ranges,
their fluctuations at each level, amount available, extent of and electricity at certain voltages. At some stages of some design
recovery of condensate, and unit costs. work, the specifications of the utilities may not have been
10. Electrical power: Voltages allowed for instruments, lighting and established. Then, suitable data may be selected from the
various driver sizes, transformer capacities, need for emergency commonly used values itemized in Table 1.9.
generator, unit costs.
11. Compressed air: capacities and pressures of plant and in- 1.12. LABORATORY AND PILOT PLANT WORK
strument air, instrument air dryer.
12. Plant site elevation. The need for knowledge of basic physical properties as a factor in
13. Soil bearing value, frost depth, ground water depth, piling equipment selection or design requires no stressing. Beyond this,
requirements, available soil test data. the state-of-the-art of design of many kinds of equipment and