Page 136 - Chemical engineering design
P. 136
116
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
See Table 3.6.
Table 3.5. Ranked order of interval temperatures
Interval Streams in
°
Rank T n C interval
175 ° C
145 30 1
140 5 4 2 C 1
85 55 3 C 4 1 C 2
55 30 3 1 C 2
25 30 3 2
Note: Duplicated temperatures are omitted. The interval
T and streams in the intervals are included as they are
needed for Table 3.6.
Table 3.6. Problem table
Interval T n CP c CP h Ł H Surplus or
Interval temp. ° C ° C kW/ ° C kW Deficit
175
1 145 30 3.0 90 s
2 140 5 0.5 2.5 d
3 85 55 2.5 137.5 d
4 55 30 2.0 60 s
5 25 30 1.0 30 d
Ł
Note: The streams in each interval are given in Table 3.5.
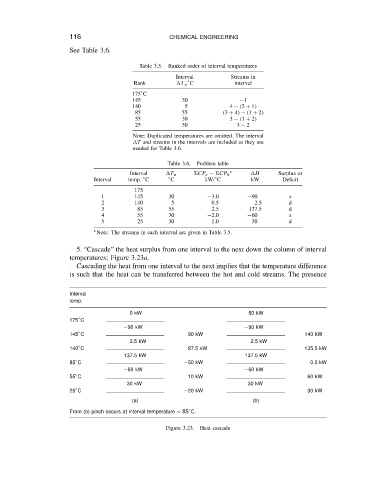
5. “Cascade” the heat surplus from one interval to the next down the column of interval
temperatures; Figure 3.23a.
Cascading the heat from one interval to the next implies that the temperature difference
is such that the heat can be transferred between the hot and cold streams. The presence
Interval
temp.
0kW 50kW
175 ° C
90 kW 90 kW
145 ° C 90 kW 140 kW
2.5 kW 2.5 kW
140 ° C 87.5 kW 135.5 kW
137.5 kW 137.5 kW
85 ° C 50 kW 0.0 kW
60 kW 60 kW
55 ° C 10 kW 60 kW
30 kW 30 kW
25 ° C 20 kW 30 kW
(a) (b)
From (b) pinch occurs at interval temperature D 85 ° C.
Figure 3.23. Heat cascade