Page 92 - Chemical equilibria Volume 4
P. 92
68 Chemical Equilibria
in the solid. In fact, the inserted atoms of H and the free sites form a solid
solution and we shall write the balance equation in the form:
2<<s>> + {H 2} = 2<<H>> [3R.2]
P/P 0
° Sieverts’ measurements
28
586K
24
565K
20
16
553K
12 523K
8
473K
4
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 x
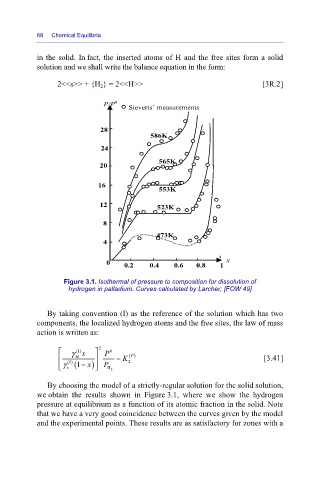
Figure 3.1. Isothermal of pressure to composition for dissolution of
hydrogen in palladium. Curves calculated by Larcher; [FOW 49]
By taking convention (I) as the reference of the solution which has two
components, the localized hydrogen atoms and the free sites, the law of mass
action is written as:
⎡ γ (I) x ⎤ 2 P 0 ()
P
⎢ H ⎥ = K 2 [3.41]
γ ⎢ (I) (1 x ⎥ ⎣ − ) P
s ⎦ H 2
By choosing the model of a strictly-regular solution for the solid solution,
we obtain the results shown in Figure 3.1, where we show the hydrogen
pressure at equilibrium as a function of its atomic fraction in the solid. Note
that we have a very good coincidence between the curves given by the model
and the experimental points. These results are as satisfactory for zones with a