Page 117 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 117
Process Circuit Analysis 101
Moist Air
Water Distributor x Water Distributor
O
-Dry Air
Louvers
Basin
Cooled Water
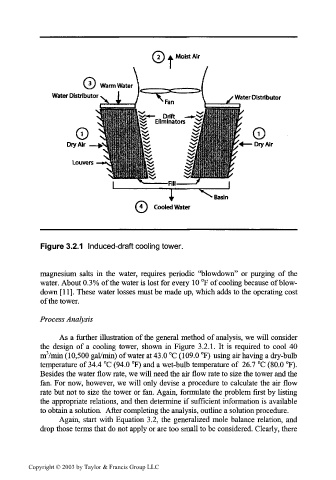
Figure 3.2.1 Induced-draft cooling tower.
magnesium salts in the water, requires periodic "blowdown" or purging of the
water. About 0.3% of the water is lost for every 10 °F of cooling because of blow-
down [11]. These water losses must be made up, which adds to the operating cost
of the tower.
Process Analysis
As a further illustration of the general method of analysis, we will consider
the design of a cooling tower, shown in Figure 3.2.1. It is required to cool 40
nrVmin (10,500 gal/min) of water at 43.0 °C (109.0 °F) using air having a dry-bulb
temperature of 34.4 °C (94.0 °F) and a wet-bulb temperature of 26.7 °C (80.0 °F).
Besides the water flow rate, we will need the air flow rate to size the tower and the
fan. For now, however, we will only devise a procedure to calculate the air flow
rate but not to size the tower or fan. Again, formulate the problem first by listing
the appropriate relations, and then determine if sufficient information is available
to obtain a solution. After completing the analysis, outline a solution procedure.
Again, start with Equation 3.2, the generalized mole balance relation, and
drop those terms that do not apply or are too small to be considered. Clearly, there
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC