Page 67 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 67
52 Chapter 2
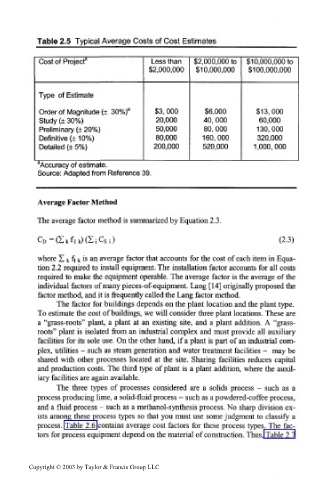
Table 2.5 Typical Average Costs of Cost Estimates
Cost of Project 3 Less than $2,000,000 to $10,000,000 to
$2,000,000 $10,000,000 $100,000,000
Type of Estimate
Order of Magnitude (± 30%) a $3, 000 $6,000 $13,000
Study (± 30%) 20,000 40, 000 60,000
Preliminary (+ 20%) 50,000 80, 000 130,000
Definitive (± 10%) 80,000 160,000 320,000
Detailed (± 5%) 200,000 520,000 1,000,000
Accuracy of estimate.
Source: Adapted from Reference 39.
Average Factor Method
The average factor method is summarized by Equation 2.3.
C D = ( Z k f l k ) ( I i C S i ) (2.3)
where Z k fi k is an average factor that accounts for the cost of each item in Equa-
tion 2.2 required to install equipment. The installation factor accounts for all costs
required to make the equipment operable. The average factor is the average of the
individual factors of many pieces-of-equipment. Lang [14] originally proposed the
factor method, and it is frequently called the Lang factor method.
The factor for buildings depends on the plant location and the plant type.
To estimate the cost of buildings, we will consider three plant locations. These are
a "grass-roots" plant, a plant at an existing site, and a plant addition. A "grass-
roots" plant is isolated from an industrial complex and must provide all auxiliary
facilities for its sole use. On the other hand, if a plant is part of an industrial com-
plex, utilities - such as steam generation and water treatment facilities - may be
shared with other processes located at the site. Sharing facilities reduces capital
and production costs. The third type of plant is a plant addition, where the auxil-
iary facilities are again available.
The three types of processes considered are a solids process - such as a
process producing lime, a solid-fluid process - such as a powdered-coffee process,
and a fluid process - such as a methanol-synthesis process. No sharp division ex-
ists among these process types so that you must use some judgment to classify a
process. Table 2.6 contains average cost factors for these process types. The fac-
tors for process equipment depend on the material of construction. Thus, Table 2.7
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC