Page 68 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 68
Production and Capital Cost Estimation 53
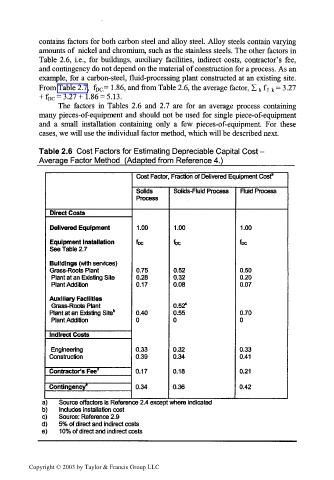
contains factors for both carbon steel and alloy steel. Alloy steels contain varying
amounts of nickel and chromium, such as the stainless steels. The other factors in
Table 2.6, i.e., for buildings, auxiliary facilities, indirect costs, contractor's fee,
and contingency do not depend on the material of construction for a process. As an
example, for a carbon-steel, fluid-processing plant constructed at an existing site.
From Table 2.7, f = 1.86, and from Table 2.6, the average factor, Z f r k = 3.27
DC k
+ f DC = 3.27+1.86 = 5.13.
The factors in Tables 2.6 and 2.7 are for an average process containing
many pieces-of-equipment and should not be used for single piece-of-equipment
and a small installation containing only a few pieces-of-equipment. For these
cases, we will use the individual factor method, which will be described next.
Table 2.6 Cost Factors for Estimating Depreciable Capital Cost -
Average Factor Method (Adapted from Reference 4.)___________
Cost Factor, Fraction of Delivered Equipment Cost"
Solids Solids-Fluid Process Fluid Process
Process
Direct Costs
Delivered Equipment 1.00 1.00 1.00
Equipment Installation foe foe fee
See Table 2.7
Buildings (with services)
Grass-Roots Plant 0.75 0.52 0.50
Plant at an Existing Site 0.28 0.32 0.20
Plant Addition 0.17 0.08 0.07
Auxiliary Facilities
Grass-Roots Plant 0.52°
Plant at an Existing Site" 0.40 0.55 0.70
Plant Addition 0 0 0
Indirect Costs
Engineering 0.33 0.32 0.33
Construction 0.39 0.34 0.41
Contractor's Fee 0 0.17 0.18 0.21
Contingency 6 0.34 0.36 0.42
i) Source offactors is Reference 2.4 except where indicated
>) Includes installation cost
,) Source: Reference 2.9
) 5% of direct and indirect costs
) 1 0% of direct and indirect costs
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC