Page 172 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 172
160 SECTION II Types of Equipment
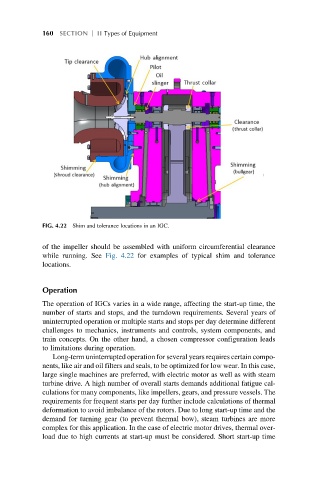
FIG. 4.22 Shim and tolerance locations in an IGC.
of the impeller should be assembled with uniform circumferential clearance
while running. See Fig. 4.22 for examples of typical shim and tolerance
locations.
Operation
The operation of IGCs varies in a wide range, affecting the start-up time, the
number of starts and stops, and the turndown requirements. Several years of
uninterrupted operation or multiple starts and stops per day determine different
challenges to mechanics, instruments and controls, system components, and
train concepts. On the other hand, a chosen compressor configuration leads
to limitations during operation.
Long-term uninterrupted operation for several years requires certain compo-
nents, like air and oil filters and seals, to be optimized for low wear. In this case,
large single machines are preferred, with electric motor as well as with steam
turbine drive. A high number of overall starts demands additional fatigue cal-
culations for many components, like impellers, gears, and pressure vessels. The
requirements for frequent starts per day further include calculations of thermal
deformation to avoid imbalance of the rotors. Due to long start-up time and the
demand for turning gear (to prevent thermal bow), steam turbines are more
complex for this application. In the case of electric motor drives, thermal over-
load due to high currents at start-up must be considered. Short start-up time