Page 358 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 358
Drivers Chapter 7 343
In VFD supplied motor applications, it is important to note that torque-speed
curves show the torque the motor can produce for each frequency, but not for
how long and if motor can operate in each condition continuously. If in a VFD
supplied motor application, a standard induction motor is used, heat limitations
need to be taken into consideration. Standard industrial motor is usually an
enclosed with an external shaft mounted fan which blows air over the finned
external case. The standard design and motor cooling is for the continuous oper-
ation for the fixed network supplied frequency and rated speed. When standard
industrial motor operates connected to a VFD which produces low frequency
and runs the motor at low speed, the motor cooling becomes an issue. The motor
will be capable to produce rated torque at low speed, but in those conditions, it
will operate at higher temperature which may significantly impact the service
life of the motor or cause overheating and motor failure.
When motor is used in VFD applications, it is important to specify operating
scenarios, design the cooling accordingly, and use motors suitable for
inverter duty.
Other than cooling, there are other considerations that must be considered in
the design when VFD-driven motors are used, such as impact of the harmonics
from the VFD to the network, cable configuration and sizing from the VFD to
the motor, etc.
Steam Turbines
A steam turbine extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and converts
this energy to mechanical work in the form of rotary motion of an output shaft.
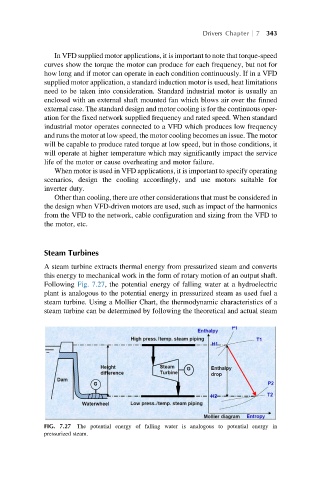
Following Fig. 7.27, the potential energy of falling water at a hydroelectric
plant is analogous to the potential energy in pressurized steam as used fuel a
steam turbine. Using a Mollier Chart, the thermodynamic characteristics of a
steam turbine can be determined by following the theoretical and actual steam
FIG. 7.27 The potential energy of falling water is analogous to potential energy in
pressurized steam.