Page 49 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 49
40 SECTION II Types of Equipment
increases in area as more flow is added in the direction of rotation. As you
approach the tongue from the other side, the goal is to have the entire flow exit
the volute, preventing recirculation of flow. Similar to an impeller, volutes have
a design point flow where they have optimized efficiency, and tend to perform
worse as flow increases or decreases away from the design point.
Collector
A collector is employed in applications where performance is not as critical.
Often, these elements are cheaper to manufacture, hence their benefit. A collec-
tor is a constant area annular cavity that the diffuser abruptly discharges into.
This abrupt transition into a slow velocity field results in irreversible losses.
Seals
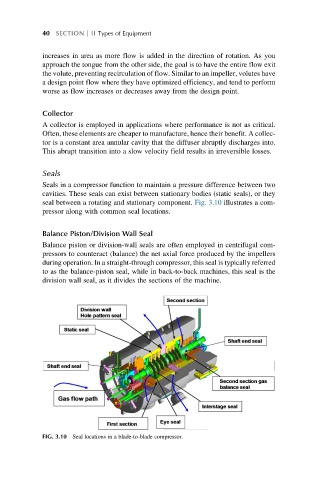
Seals in a compressor function to maintain a pressure difference between two
cavities. These seals can exist between stationary bodies (static seals), or they
seal between a rotating and stationary component. Fig. 3.10 illustrates a com-
pressor along with common seal locations.
Balance Piston/Division Wall Seal
Balance piston or division-wall seals are often employed in centrifugal com-
pressors to counteract (balance) the net axial force produced by the impellers
during operation. In a straight-through compressor, this seal is typically referred
to as the balance-piston seal, while in back-to-back machines, this seal is the
division wall seal, as it divides the sections of the machine.
FIG. 3.10 Seal locations in a blade-to-blade compressor.