Page 145 -
P. 145
116 CHAPTER 4 / CACHE MEMORY
Example 4.1 Suppose that the processor has access to two levels of memory. Level 1
contains 1000 words and has an access time of 0.01 s; level 2 contains 100,000 words and
m
m
has an access time of 0.1 s. Assume that if a word to be accessed is in level 1, then the
processor accesses it directly. If it is in level 2, then the word is first transferred to level 1
and then accessed by the processor. For simplicity, we ignore the time required for the
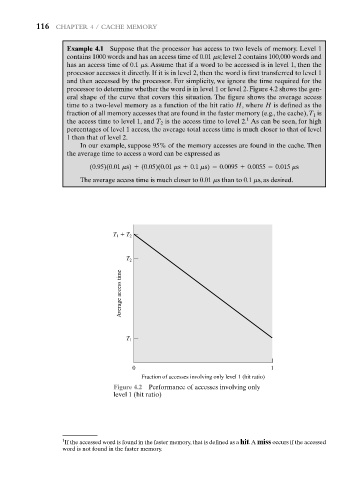
processor to determine whether the word is in level 1 or level 2. Figure 4.2 shows the gen-
eral shape of the curve that covers this situation. The figure shows the average access
time to a two-level memory as a function of the hit ratio H, where H is defined as the
fraction of all memory accesses that are found in the faster memory (e.g., the cache), T 1 is
1
the access time to level 1, and T 2 is the access time to level 2. As can be seen, for high
percentages of level 1 access, the average total access time is much closer to that of level
1 than that of level 2.
In our example, suppose 95% of the memory accesses are found in the cache. Then
the average time to access a word can be expressed as
(0.95)(0.01 ms) + (0.05)(0.01 ms + 0.1 ms) = 0.0095 + 0.0055 = 0.015 ms
The average access time is much closer to 0.01 s than to 0.1 s, as desired.mm
T 1 T 2
T 2
Average access time
T 1
0 1
Fraction of accesses involving only level 1 (hit ratio)
Figure 4.2 Performance of accesses involving only
level 1 (hit ratio)
1 If the accessed word is found in the faster memory, that is defined as a hit.A miss occurs if the accessed
word is not found in the faster memory.