Page 149 -
P. 149
120 CHAPTER 4 / CACHE MEMORY
whether the line has been modified since being loaded into the cache.The length of
a line, not including tag and control bits, is the line size.The line size may be as small
as 32 bits, with each “word” being a single byte; in this case the line size is 4 bytes.
The number of lines is considerably less than the number of main memory blocks
(m V M).At any time, some subset of the blocks of memory resides in lines in the
cache. If a word in a block of memory is read, that block is transferred to one of the
lines of the cache. Because there are more blocks than lines, an individual line can-
not be uniquely and permanently dedicated to a particular block.Thus, each line in-
cludes a tag that identifies which particular block is currently being stored. The tag
is usually a portion of the main memory address, as described later in this section.
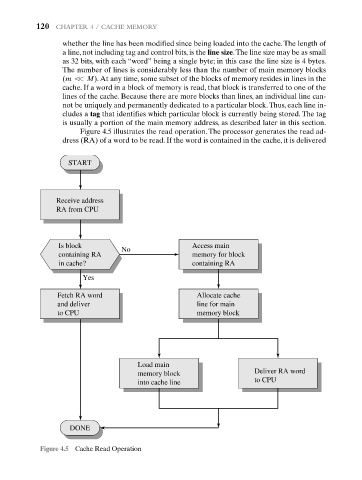
Figure 4.5 illustrates the read operation. The processor generates the read ad-
dress (RA) of a word to be read. If the word is contained in the cache, it is delivered
START
Receive address
RA from CPU
Is block Access main
No
containing RA memory for block
in cache? containing RA
Yes
Fetch RA word Allocate cache
and deliver line for main
to CPU memory block
Load main
Deliver RA word
memory block
to CPU
into cache line
DONE
Figure 4.5 Cache Read Operation