Page 152 -
P. 152
4.3 / ELEMENTS OF CACHE DESIGN 123
Logical address Physical address
MMU
Main
Processor
Cache memory
Data
(a) Logical cache
Logical address Physical address
MMU
Main
Processor
memory
Cache
Data
(b) Physical cache
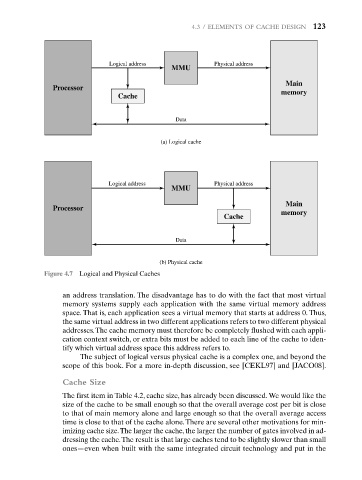
Figure 4.7 Logical and Physical Caches
an address translation. The disadvantage has to do with the fact that most virtual
memory systems supply each application with the same virtual memory address
space. That is, each application sees a virtual memory that starts at address 0. Thus,
the same virtual address in two different applications refers to two different physical
addresses.The cache memory must therefore be completely flushed with each appli-
cation context switch, or extra bits must be added to each line of the cache to iden-
tify which virtual address space this address refers to.
The subject of logical versus physical cache is a complex one, and beyond the
scope of this book. For a more in-depth discussion, see [CEKL97] and [JACO08].
Cache Size
The first item in Table 4.2, cache size, has already been discussed.We would like the
size of the cache to be small enough so that the overall average cost per bit is close
to that of main memory alone and large enough so that the overall average access
time is close to that of the cache alone.There are several other motivations for min-
imizing cache size.The larger the cache, the larger the number of gates involved in ad-
dressing the cache.The result is that large caches tend to be slightly slower than small
ones—even when built with the same integrated circuit technology and put in the