Page 157 -
P. 157
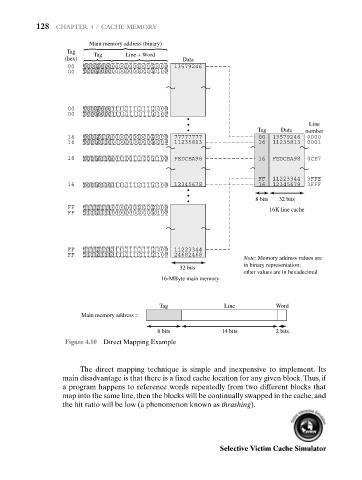
128 CHAPTER 4 / CACHE MEMORY
Main memory address (binary)
Tag
Tag Line + Word
(hex) Data
00 000000000000000000000000 13579246
00 000000000000000000000100
00 000000001111111111111000
00 000000001111111111111100
Line
Tag Data number
16 000101100000000000000000 77777777 00 13579246 0000
16 000101100000000000000004 11235813 16 11235813 0001
16 000101100011001110011100 FEDCBA98 16 FEDCBA98 0CE7
FEDCBA98
FF 11223344 3FFE
16 000101101111111111111100 12345678 16 12345678 3FFF
8 bits 32 bits
FF 111111110000000000000000 16K line cache
FF 111111110000000000000100
FF 111111111111111111111000 11223344
FF 111111111111111111111100 24682468
Note: Memory address values are
in binary representation;
32 bits
other values are in hexadecimal
16-MByte main memory
Tag Line Word
Main memory address =
8 bits 14 bits 2 bits
Figure 4.10 Direct Mapping Example
The direct mapping technique is simple and inexpensive to implement. Its
main disadvantage is that there is a fixed cache location for any given block.Thus, if
a program happens to reference words repeatedly from two different blocks that
map into the same line, then the blocks will be continually swapped in the cache, and
the hit ratio will be low (a phenomenon known as thrashing).
Selective Victim Cache Simulator