Page 155 -
P. 155
126 CHAPTER 4 / CACHE MEMORY
b t b
B 0 L 0
m lines
B m–1
L m–1
First m blocks of Cache memory
main memory
(equal to size of cache) b = length of block in bits
t = length of tag in bits
(a) Direct mapping
t b
L 0
b
One block of
main memory
L m–1
Cache memory
(b) Associative mapping
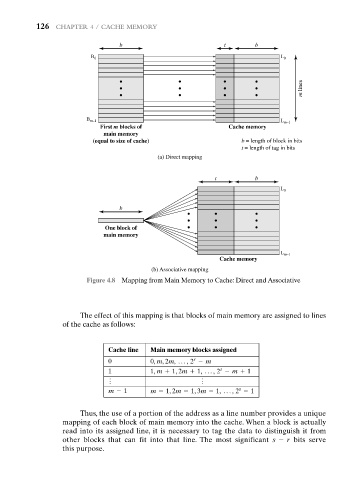
Figure 4.8 Mapping from Main Memory to Cache: Direct and Associative
The effect of this mapping is that blocks of main memory are assigned to lines
of the cache as follows:
Cache line Main memory blocks assigned
s
0 0, m,2m, Á , 2 - m
s
1 1, m + 1, 2m + 1, Á , 2 - m + 1
o o
s
m - 1 m - 1, 2m - 1, 3m - 1, Á , 2 - 1
Thus, the use of a portion of the address as a line number provides a unique
mapping of each block of main memory into the cache. When a block is actually
read into its assigned line, it is necessary to tag the data to distinguish it from
other blocks that can fit into that line. The most significant s - r bits serve
this purpose.