Page 153 -
P. 153
124 CHAPTER 4 / CACHE MEMORY
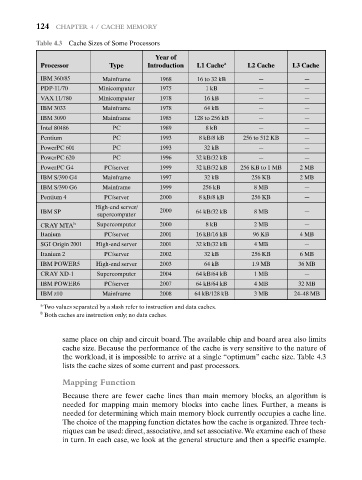
Table 4.3 Cache Sizes of Some Processors
Year of
Processor Type Introduction L1 Cache a L2 Cache L3 Cache
IBM 360/85 Mainframe 1968 16 to 32 kB — —
PDP-11/70 Minicomputer 1975 1 kB — —
VAX 11/780 Minicomputer 1978 16 kB — —
IBM 3033 Mainframe 1978 64 kB — —
IBM 3090 Mainframe 1985 128 to 256 kB — —
Intel 80486 PC 1989 8 kB — —
Pentium PC 1993 8 kB/8 kB 256 to 512 KB —
PowerPC 601 PC 1993 32 kB — —
PowerPC 620 PC 1996 32 kB/32 kB — —
PowerPC G4 PC/server 1999 32 kB/32 kB 256 KB to 1 MB 2 MB
IBM S/390 G4 Mainframe 1997 32 kB 256 KB 2 MB
IBM S/390 G6 Mainframe 1999 256 kB 8 MB —
Pentium 4 PC/server 2000 8 kB/8 kB 256 KB —
High-end server/
IBM SP 2000 64 kB/32 kB 8 MB —
supercomputer
CRAY MTA b Supercomputer 2000 8 kB 2 MB —
Itanium PC/server 2001 16 kB/16 kB 96 KB 4 MB
SGI Origin 2001 High-end server 2001 32 kB/32 kB 4 MB —
Itanium 2 PC/server 2002 32 kB 256 KB 6 MB
IBM POWER5 High-end server 2003 64 kB 1.9 MB 36 MB
CRAY XD-1 Supercomputer 2004 64 kB/64 kB 1 MB —
IBM POWER6 PC/server 2007 64 kB/64 kB 4 MB 32 MB
IBM z10 Mainframe 2008 64 kB/128 kB 3 MB 24–48 MB
a
Two values separated by a slash refer to instruction and data caches.
b
Both caches are instruction only; no data caches.
same place on chip and circuit board. The available chip and board area also limits
cache size. Because the performance of the cache is very sensitive to the nature of
the workload, it is impossible to arrive at a single “optimum” cache size. Table 4.3
lists the cache sizes of some current and past processors.
Mapping Function
Because there are fewer cache lines than main memory blocks, an algorithm is
needed for mapping main memory blocks into cache lines. Further, a means is
needed for determining which main memory block currently occupies a cache line.
The choice of the mapping function dictates how the cache is organized.Three tech-
niques can be used: direct, associative, and set associative.We examine each of these
in turn. In each case, we look at the general structure and then a specific example.