Page 221 -
P. 221
6.1 / MAGNETIC DISK 189
Index
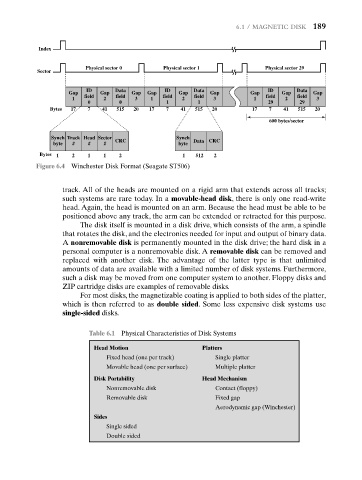
Physical sector 0 Physical sector 1 Physical sector 29
Sector
ID Data ID Data ID Data
Gap Gap Gap Gap Gap Gap Gap Gap Gap
1 field 2 field 3 1 field 2 field 3 1 field 2 field 3
0 0 1 1 29 29
Bytes 17 7 41 515 20 17 7 41 515 20 17 7 41 515 20
600 bytes/sector
Synch Track Head Sector CRC Synch
byte # # # byte Data CRC
Bytes 1 2 1 1 2 1 512 2
Figure 6.4 Winchester Disk Format (Seagate ST506)
track. All of the heads are mounted on a rigid arm that extends across all tracks;
such systems are rare today. In a movable-head disk, there is only one read-write
head. Again, the head is mounted on an arm. Because the head must be able to be
positioned above any track, the arm can be extended or retracted for this purpose.
The disk itself is mounted in a disk drive, which consists of the arm, a spindle
that rotates the disk, and the electronics needed for input and output of binary data.
A nonremovable disk is permanently mounted in the disk drive; the hard disk in a
personal computer is a nonremovable disk. A removable disk can be removed and
replaced with another disk. The advantage of the latter type is that unlimited
amounts of data are available with a limited number of disk systems. Furthermore,
such a disk may be moved from one computer system to another. Floppy disks and
ZIP cartridge disks are examples of removable disks.
For most disks, the magnetizable coating is applied to both sides of the platter,
which is then referred to as double sided. Some less expensive disk systems use
single-sided disks.
Table 6.1 Physical Characteristics of Disk Systems
Head Motion Platters
Fixed head (one per track) Single platter
Movable head (one per surface) Multiple platter
Disk Portability Head Mechanism
Nonremovable disk Contact (floppy)
Removable disk Fixed gap
Aerodynamic gap (Winchester)
Sides
Single sided
Double sided