Page 218 -
P. 218
186 CHAPTER 6 / EXTERNAL MEMORY
Read
current
MR
sensor Write current
Track width Shield
Inductive
N
write element
S
S
N
N
Magnetization S
S
N
N
S
S
N
N
S
Recording
medium
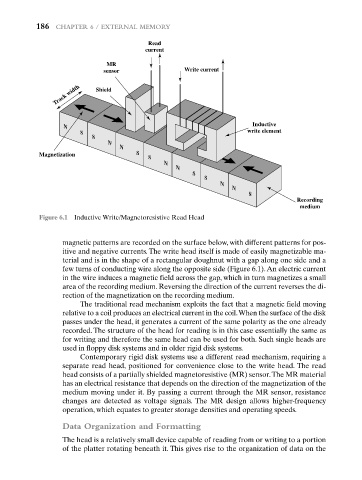
Figure 6.1 Inductive Write/Magnetoresistive Read Head
magnetic patterns are recorded on the surface below, with different patterns for pos-
itive and negative currents. The write head itself is made of easily magnetizable ma-
terial and is in the shape of a rectangular doughnut with a gap along one side and a
few turns of conducting wire along the opposite side (Figure 6.1).An electric current
in the wire induces a magnetic field across the gap, which in turn magnetizes a small
area of the recording medium. Reversing the direction of the current reverses the di-
rection of the magnetization on the recording medium.
The traditional read mechanism exploits the fact that a magnetic field moving
relative to a coil produces an electrical current in the coil.When the surface of the disk
passes under the head, it generates a current of the same polarity as the one already
recorded. The structure of the head for reading is in this case essentially the same as
for writing and therefore the same head can be used for both. Such single heads are
used in floppy disk systems and in older rigid disk systems.
Contemporary rigid disk systems use a different read mechanism, requiring a
separate read head, positioned for convenience close to the write head. The read
head consists of a partially shielded magnetoresistive (MR) sensor.The MR material
has an electrical resistance that depends on the direction of the magnetization of the
medium moving under it. By passing a current through the MR sensor, resistance
changes are detected as voltage signals. The MR design allows higher-frequency
operation, which equates to greater storage densities and operating speeds.
Data Organization and Formatting
The head is a relatively small device capable of reading from or writing to a portion
of the platter rotating beneath it. This gives rise to the organization of data on the