Page 214 -
P. 214
182 CHAPTER 5 / INTERNAL MEMORY
propagation delays along the data paths (from memory to processor) and processor
data hold time requirements.Assume a clocking rate of 10 MHz.
a. How fast (access time) should the DRAMs be if no wait states are to be inserted?
b. How many wait states do we have to insert per memory read operation if the ac-
cess time of the DRAMs is 150 ns?
5.6 The memory of a particular microcomputer is built from 64K * 1 DRAMs. Accord-
ing to the data sheet, the cell array of the DRAM is organized into 256 rows. Each
row must be refreshed at least once every 4 ms. Suppose we refresh the memory on a
strictly periodic basis.
a. What is the time period between successive refresh requests?
b. How long a refresh address counter do we need?
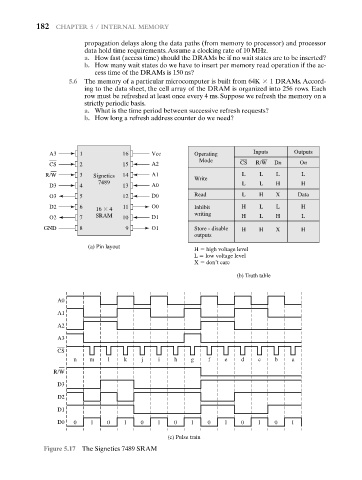
A3 1 16 Vcc Operating Inputs Outputs
Mode CS R/W Dn On
CS 2 15 A2
R/W 3 Signetics 14 A1 L L L L
Write
7489 L L H H
D3 4 13 A0
O3 5 12 D0 Read L H X Data
D2 6 16 4 11 O0 Inhibit H L L H
O2 7 SRAM 10 D1 writing H L H L
GND 8 9 O1 Store - disable H H X H
outputs
H high voltage level
L low voltage level
X don’t care
(b) Truth table
A0
A1
A2
A3
CS
n m l k j i h g f e d c b a
R/W
D3
D2
D1
D0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
(c) Pulse train
Figure 5.17 The Signetics 7489 SRAM