Page 220 -
P. 220
4.1 Points and patches 199
(a) image gradients (b) keypoint descriptor
Figure 4.19 The gradient location-orientation histogram (GLOH) descriptor uses log-polar bins instead of square
bins to compute orientation histograms (Mikolajczyk and Schmid 2005).
(a) (b)
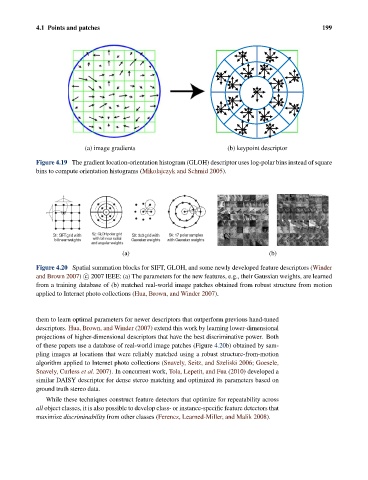
Figure 4.20 Spatial summation blocks for SIFT, GLOH, and some newly developed feature descriptors (Winder
and Brown 2007) c 2007 IEEE: (a) The parameters for the new features, e.g., their Gaussian weights, are learned
from a training database of (b) matched real-world image patches obtained from robust structure from motion
applied to Internet photo collections (Hua, Brown, and Winder 2007).
them to learn optimal parameters for newer descriptors that outperform previous hand-tuned
descriptors. Hua, Brown, and Winder (2007) extend this work by learning lower-dimensional
projections of higher-dimensional descriptors that have the best discriminative power. Both
of these papers use a database of real-world image patches (Figure 4.20b) obtained by sam-
pling images at locations that were reliably matched using a robust structure-from-motion
algorithm applied to Internet photo collections (Snavely, Seitz, and Szeliski 2006; Goesele,
Snavely, Curless et al. 2007). In concurrent work, Tola, Lepetit, and Fua (2010) developed a
similar DAISY descriptor for dense stereo matching and optimized its parameters based on
ground truth stereo data.
While these techniques construct feature detectors that optimize for repeatability across
all object classes, it is also possible to develop class- or instance-specific feature detectors that
maximize discriminability from other classes (Ferencz, Learned-Miller, and Malik 2008).