Page 353 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 353
Vision System
(SEM) chips and biochips raise hopes of computers rivaling the human
brain in terms of data density. Processing speed, too, keeps increasing, as
clock speeds get faster and data buses get wider.Nevertheless,expectations
in VR have historically run ahead of the technology.
Reactions: Some technophiles find VR so compelling that they use it as
an escape from reality,rather than as an entertainment device.Proponents
of VR argue that this does not reflect a problem with VR, any more than
“computer addiction”represents a problem with computers. The trouble,
say these researchers, is in the minds of people who are maladjusted to
begin with. Other people are afraid of VR experiences; some VR illusions
are as intense as hallucinations caused by drugs. Another problem results
from the uncanny valley phenomenon, in which people become appre-
hensive around smart machines.
See also UNCANNY VALLEY THEORY and TELEPRESENCE.
VISION SYSTEM
One of the most advanced features of a mobile robot is the vision system,
also called machine vision. There are several different designs; the optimum
design depends on the application.
Components of a visible-light system
A visible-light vision system must have a device for receiving incoming
images. This is usually a vidicon or charge-coupled device video camera. In
bright light an image orthicon can be used.
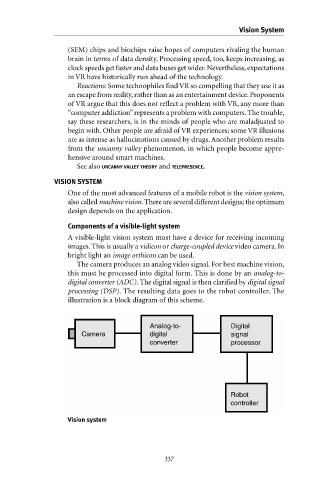
The camera produces an analog video signal. For best machine vision,
this must be processed into digital form. This is done by an analog-to-
digital converter (ADC). The digital signal is then clarified by digital signal
processing (DSP). The resulting data goes to the robot controller. The
illustration is a block diagram of this scheme.
Analog-to- Digital
Camera digital signal
converter processor
Robot
controller
Vision system