Page 128 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 128
114 Control theory in biomedical engineering
target output vector in an input data matrix. This input matrix will be used to
evaluate the FLC performances by comparing predicted outputs with their
corresponding targets.
2.2 Fuzzy arrhythmia classification
After pre-processing, the obtained feature vectors are treated by the FLC for
the patient’s arrhythmia classification. However, the FLC necessitates two
major steps first: configuration and optimization.
2.2.1 FLC configuration
A standard controller requires the most accurate model by using differential
equations. However, a FLC does not require a mathematical model, but it
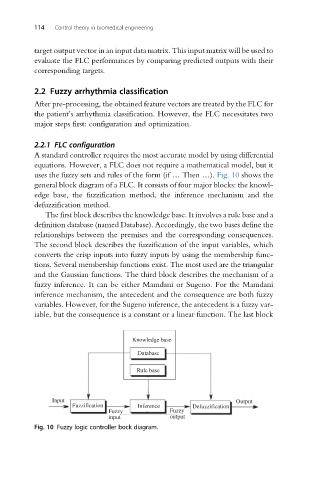
uses the fuzzy sets and rules of the form (if … Then …). Fig. 10 shows the
general block diagram of a FLC. It consists of four major blocks: the knowl-
edge base, the fuzzification method, the inference mechanism and the
defuzzification method.
The first block describes the knowledge base. It involves a rule base and a
definition database (named Database). Accordingly, the two bases define the
relationships between the premises and the corresponding consequences.
The second block describes the fuzzification of the input variables, which
converts the crisp inputs into fuzzy inputs by using the membership func-
tions. Several membership functions exist. The most used are the triangular
and the Gaussian functions. The third block describes the mechanism of a
fuzzy inference. It can be either Mamdani or Sugeno. For the Mamdani
inference mechanism, the antecedent and the consequence are both fuzzy
variables. However, for the Sugeno inference, the antecedent is a fuzzy var-
iable, but the consequence is a constant or a linear function. The last block
Knowledge base
Database
Rule base
Input Output
Fuzzification Inference Defuzzification
Fuzzy Fuzzy
input output
Fig. 10 Fuzzy logic controller bock diagram.