Page 239 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 239
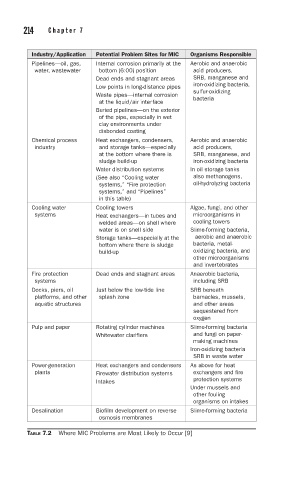
214 C h a p t e r 7 C o r r o s i o n F a i l u r e s , F a c t o r s , a n d C e l l s 215
Industry/Application Potential Problem Sites for MIC Organisms Responsible
Pipelines—oil, gas, Internal corrosion primarily at the Aerobic and anaerobic
water, wastewater bottom (6:00) position acid producers,
Dead ends and stagnant areas SRB, manganese and
Low points in long-distance pipes iron-oxidizing bacteria,
Waste pipes—internal corrosion sulfur-oxidizing
bacteria
at the liquid/air interface
Buried pipelines—on the exterior
of the pipe, especially in wet
clay environments under
disbonded coating
Chemical process Heat exchangers, condensers, Aerobic and anaerobic
industry and storage tanks—especially acid producers,
at the bottom where there is SRB, manganese, and
sludge build-up iron-oxidizing bacteria
Water distribution systems In oil storage tanks
(See also “Cooling water also methanogens,
systems,” “Fire protection oil-hydrolyzing bacteria
systems,” and “Pipelines”
in this table)
Cooling water Cooling towers Algae, fungi, and other
systems Heat exchangers—in tubes and microorganisms in
welded areas—on shell where cooling towers
water is on shell side Slime-forming bacteria,
Storage tanks—especially at the aerobic and anaerobic
bottom where there is sludge bacteria, metal-
build-up oxidizing bacteria, and
other microorganisms
and invertebrates
Fire protection Dead ends and stagnant areas Anaerobic bacteria,
systems including SRB
Docks, piers, oil Just below the low-tide line SRB beneath
platforms, and other splash zone barnacles, mussels,
aquatic structures and other areas
sequestered from
oxygen
Pulp and paper Rotating cylinder machines Slime-forming bacteria
Whitewater clarifiers and fungi on paper-
making machines
Iron-oxidizing bacteria
SRB in waste water
Power-generation Heat exchangers and condensers As above for heat
plants Firewater distribution systems exchangers and fire
Intakes protection systems
Under mussels and
other fouling
organisms on intakes
Desalination Biofilm development on reverse Slime-forming bacteria
osmosis membranes
TABLE 7.2 Where MIC Problems are Most Likely to Occur [9]