Page 243 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 243
218 C h a p t e r 7 C o r r o s i o n F a i l u r e s , F a c t o r s , a n d C e l l s 219
[2]
Prior chemistry history
[5] [7]
[1] Transformations Inhibition
Nominal
chemistry
major
minor
LA i
Physical features Concentration LA Result
i
[4] [6] [8]
System sources
[3]
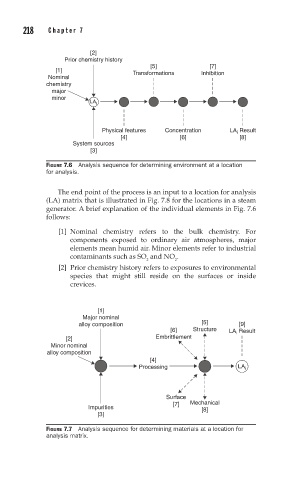
FIGURE 7.6 Analysis sequence for determining environment at a location
for analysis.
The end point of the process is an input to a location for analysis
(LA) matrix that is illustrated in Fig. 7.8 for the locations in a steam
generator. A brief explanation of the individual elements in Fig. 7.6
follows:
[1] Nominal chemistry refers to the bulk chemistry. For
components exposed to ordinary air atmospheres, major
elements mean humid air. Minor elements refer to industrial
contaminants such as SO and NO .
2 2
[2] Prior chemistry history refers to exposures to environmental
species that might still reside on the surfaces or inside
crevices.
[1]
Major nominal
alloy composition [5] [9]
[6] Structure LA Result
i
[2] Embrittlement
Minor nominal
alloy composition
[4]
Processing LA i
Surface
[7] Mechanical
Impurities [8]
[3]
FIGURE 7.7 Analysis sequence for determining materials at a location for
analysis matrix.