Page 244 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 244
218 C h a p t e r 7 C o r r o s i o n F a i l u r e s , F a c t o r s , a n d C e l l s 219
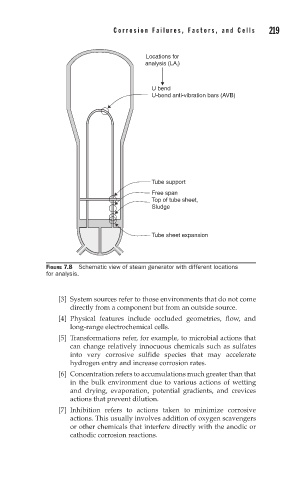
Locations for
analysis (LA ) i
U bend
U-bend anti-vibration bars (AVB)
Tube support
Free span
Top of tube sheet,
Sludge
Tube sheet expansion
FIGURE 7.8 Schematic view of steam generator with different locations
for analysis.
[3] System sources refer to those environments that do not come
directly from a component but from an outside source.
[4] Physical features include occluded geometries, flow, and
long-range electrochemical cells.
[5] Transformations refer, for example, to microbial actions that
can change relatively innocuous chemicals such as sulfates
into very corrosive sulfide species that may accelerate
hydrogen entry and increase corrosion rates.
[6] Concentration refers to accumulations much greater than that
in the bulk environment due to various actions of wetting
and drying, evaporation, potential gradients, and crevices
actions that prevent dilution.
[7] Inhibition refers to actions taken to minimize corrosive
actions. This usually involves addition of oxygen scavengers
or other chemicals that interfere directly with the anodic or
cathodic corrosion reactions.