Page 254 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 254
228 C h a p t e r 7 C o r r o s i o n F a i l u r e s , F a c t o r s , a n d C e l l s 229
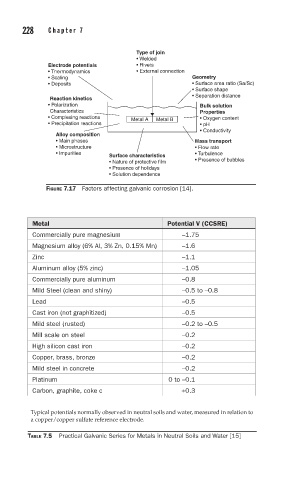
Type of join
• Welded
Electrode potentials • Rivets
• Thermodynamics • External connection
• Scaling Geometry
• Deposits • Surface area ratio (Sa/Sc)
• Surface shape
• Separation distance
Reaction kinetics
• Polarization Bulk solution
Characteristics Properties
• Complexing reactions Metal A Metal B • Oxygen content
• Precipitation reactions • pH
• Conductivity
Alloy composition
• Main phases Mass transport
• Microstructure • Flow rate
• Impurities Surface characteristics • Turbulence
• Nature of protective film • Presence of bubbles
• Presence of holidays
• Solution dependence
FIGURE 7.17 Factors affecting galvanic corrosion [14].
Metal Potential V (CCSRE)
Commercially pure magnesium –1.75
Magnesium alloy (6% Al, 3% Zn, 0.15% Mn) –1.6
Zinc –1.1
Aluminum alloy (5% zinc) –1.05
Commercially pure aluminum –0.8
Mild Steel (clean and shiny) –0.5 to –0.8
Lead –0.5
Cast iron (not graphitized) –0.5
Mild steel (rusted) –0.2 to –0.5
Mill scale on steel –0.2
High silicon cast iron –0.2
Copper, brass, bronze –0.2
Mild steel in concrete –0.2
Platinum 0 to –0.1
Carbon, graphite, coke c +0.3
Typical potentials normally observed in neutral soils and water, measured in relation to
a copper/copper sulfate reference electrode.
TABLE 7.5 Practical Galvanic Series for Metals in Neutral Soils and Water [15]