Page 352 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 352
322 C h a p t e r 8 C o r r o s i o n b y W a t e r 323
3.5
3
2.5
Degree of saturation 1.5
2
1
0
0.5 17
33
50
0 67 % Injection
25 42 83
58 75 100
Temperature 92 108 125
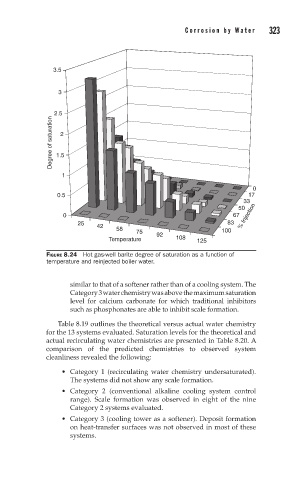
FIGURE 8.24 Hot gas-well barite degree of saturation as a function of
temperature and reinjected boiler water.
similar to that of a softener rather than of a cooling system. The
Category 3 water chemistry was above the maximum saturation
level for calcium carbonate for which traditional inhibitors
such as phosphonates are able to inhibit scale formation.
Table 8.19 outlines the theoretical versus actual water chemistry
for the 13 systems evaluated. Saturation levels for the theoretical and
actual recirculating water chemistries are presented in Table 8.20. A
comparison of the predicted chemistries to observed system
cleanliness revealed the following:
• Category 1 (recirculating water chemistry undersaturated).
The systems did not show any scale formation.
• Category 2 (conventional alkaline cooling system control
range). Scale formation was observed in eight of the nine
Category 2 systems evaluated.
• Category 3 (cooling tower as a softener). Deposit formation
on heat-transfer surfaces was not observed in most of these
systems.