Page 751 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 751
702 C h a p t e r 1 5 H i g h - Te m p e r a t u r e C o r r o s i o n 703
10.0
9.0
8.0
ACI HK
7.0
ACI HP Nb
Alloy 800H
6.0
Penetration (mm) 5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0.0
820 870 920 970 1020 1070
Temperature (°C)
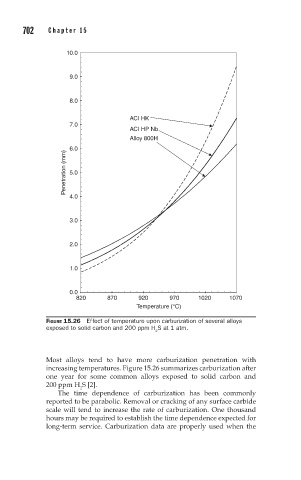
FIGURE 15.26 Effect of temperature upon carburization of several alloys
exposed to solid carbon and 200 ppm H S at 1 atm.
2
Most alloys tend to have more carburization penetration with
increasing temperatures. Figure 15.26 summarizes carburization after
one year for some common alloys exposed to solid carbon and
200 ppm H S [2].
2
The time dependence of carburization has been commonly
reported to be parabolic. Removal or cracking of any surface carbide
scale will tend to increase the rate of carburization. One thousand
hours may be required to establish the time dependence expected for
long-term service. Carburization data are properly used when the