Page 33 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 33
18 Chapter 1 DSP Integrated Circuits
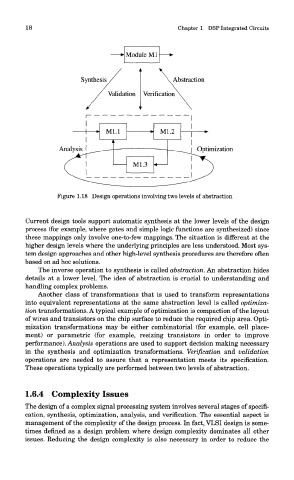
Figure 1.18 Design operations involving two levels of abstraction
Current design tools support automatic synthesis at the lower levels of the design
process (for example, where gates and simple logic functions are synthesized) since
these mappings only involve one-to-few mappings. The situation is different at the
higher design levels where the underlying principles are less understood. Most sys-
tem design approaches and other high-level synthesis procedures are therefore often
based on ad hoc solutions.
The inverse operation to synthesis is called abstraction. An abstraction hides
details at a lower level. The idea of abstraction is crucial to understanding and
handling complex problems.
Another class of transformations that is used to transform representations
into equivalent representations at the same abstraction level is called optimiza-
tion transformations. A typical example of optimization is compaction of the layout
of wires and transistors on the chip surface to reduce the required chip area. Opti-
mization transformations may be either combinatorial (for example, cell place-
ment) or parametric (for example, resizing transistors in order to improve
performance). Analysis operations are used to support decision making necessary
in the synthesis and optimization transformations. Verification and validation
operations are needed to assure that a representation meets its specification.
These operations typically are performed between two levels of abstraction.
1.6.4 Complexity Issues
The design of a complex signal processing system involves several stages of specifi-
cation, synthesis, optimization, analysis, and verification. The essential aspect is
management of the complexity of the design process. In fact, VLSI design is some-
times defined as a design problem where design complexity dominates all other
issues. Reducing the design complexity is also necessary in order to reduce the