Page 549 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 549
534 Chapter 12 Integrated Circuit Design
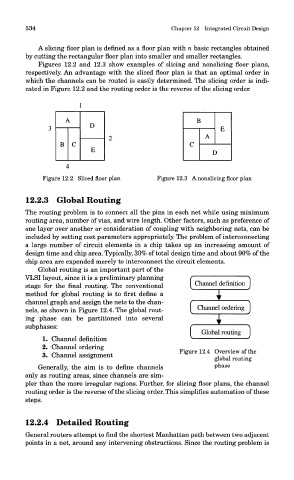
A slicing floor plan is defined as a floor plan with n basic rectangles obtained
by cutting the rectangular floor plan into smaller and smaller rectangles.
Figures 12.2 and 12.3 show examples of slicing and nonslicing floor plans,
respectively. An advantage with the sliced floor plan is that an optimal order in
which the channels can be routed is easily determined. The slicing order is indi-
cated in Figure 12.2 and the routing order is the reverse of the slicing order.
Figure 12.2 Sliced floor plan Figure 12.3 A nonslicing floor plan
12.2.3 Global Routing
The routing problem is to connect all the pins in each net while using minimum
routing area, number of vias, and wire length. Other factors, such as preference of
one layer over another or consideration of coupling with neighboring nets, can be
included by setting cost parameters appropriately. The problem of interconnecting
a large number of circuit elements in a chip takes up an increasing amount of
design time and chip area. Typically, 30% of total design time and about 90% of the
chip area are expended merely to interconnect the circuit elements.
Global routing is an important part of the
VLSI layout, since it is a preliminary planning
stage for the final routing. The conventional
method for global routing is to first define a
channel graph and assign the nets to the chan-
nels, as shown in Figure 12.4. The global rout-
ing phase can be partitioned into several
subphases:
1. Channel definition
2. Channel ordering
Figure 12.4 Overview of the
3. Channel assignment
global routing
Generally, the aim is to define channels phase
only as routing areas, since channels are sim-
pler than the more irregular regions. Further, for slicing floor plans, the channel
routing order is the reverse of the slicing order. This simplifies automation of these
steps.
12.2.4 Detailed Routing
General routers attempt to find the shortest Manhattan path between two adjacent
points in a net, around any intervening obstructions. Since the routing problem is