Page 266 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 266
Distributed generation in deregulated Chapter | 9 229
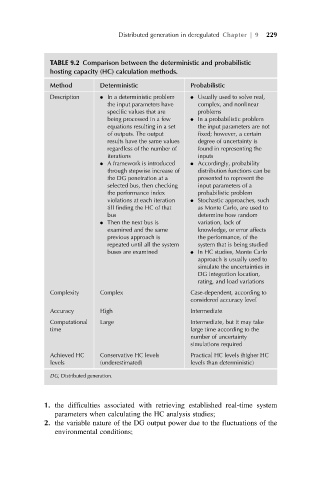
TABLE 9.2 Comparison between the deterministic and probabilistic
hosting capacity (HC) calculation methods.
Method Deterministic Probabilistic
Description In a deterministic problem Usually used to solve real,
the input parameters have complex, and nonlinear
specific values that are problems
being processed in a few In a probabilistic problem
equations resulting in a set the input parameters are not
of outputs. The output fixed; however, a certain
results have the same values degree of uncertainty is
regardless of the number of found in representing the
iterations inputs
A framework is introduced Accordingly, probability
through stepwise increase of distribution functions can be
the DG penetration at a presented to represent the
selected bus, then checking input parameters of a
the performance index probabilistic problem
violations at each iteration Stochastic approaches, such
till finding the HC of that as Monte Carlo, are used to
bus determine how random
Then the next bus is variation, lack of
examined and the same knowledge, or error affects
previous approach is the performance, of the
repeated until all the system system that is being studied
buses are examined In HC studies, Monte Carlo
approach is usually used to
simulate the uncertainties in
DG integration location,
rating, and load variations
Complexity Complex Case-dependent, according to
considered accuracy level
Accuracy High Intermediate
Computational Large Intermediate, but it may take
time large time according to the
number of uncertainty
simulations required
Achieved HC Conservative HC levels Practical HC levels (higher HC
levels (underestimated) levels than deterministic)
DG, Distributed generation.
1. the difficulties associated with retrieving established real-time system
parameters when calculating the HC analysis studies;
2. the variable nature of the DG output power due to the fluctuations of the
environmental conditions;