Page 346 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 346
308 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
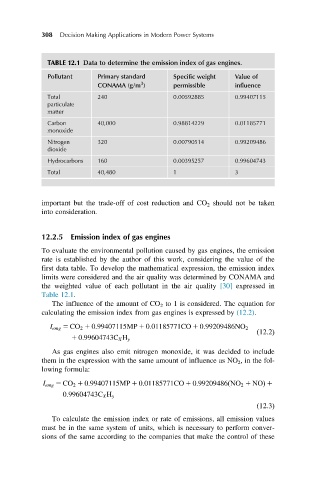
TABLE 12.1 Data to determine the emission index of gas engines.
Pollutant Primary standard Specific weight Value of
3
CONAMA (g/m ) permissible influence
Total 240 0.00592885 0.99407115
particulate
matter
Carbon 40,000 0.98814229 0.01185771
monoxide
Nitrogen 320 0.00790514 0.99209486
dioxide
Hydrocarbons 160 0.00395257 0.99604743
Total 40,480 1 3
important but the trade-off of cost reduction and CO 2 should not be taken
into consideration.
12.2.5 Emission index of gas engines
To evaluate the environmental pollution caused by gas engines, the emission
rate is established by the author of this work, considering the value of the
first data table. To develop the mathematical expression, the emission index
limits were considered and the air quality was determined by CONAMA and
the weighted value of each pollutant in the air quality [30] expressed in
Table 12.1.
The influence of the amount of CO 2 to 1 is considered. The equation for
calculating the emission index from gas engines is expressed by (12.2).
I emg 5 CO 2 1 0:99407115MP 1 0:01185771CO 1 0:99209486NO 2
ð12:2Þ
1 0:99604743C X H y
As gas engines also emit nitrogen monoxide, it was decided to include
them in the expression with the same amount of influence as NO 2 , in the fol-
lowing formula:
I emg 5 CO 2 1 0:99407115MP 1 0:01185771CO 1 0:99209486ðNO 2 1 NOÞ 1
0:99604743C X H y
ð12:3Þ
To calculate the emission index or rate of emissions, all emission values
must be in the same system of units, which is necessary to perform conver-
sions of the same according to the companies that make the control of these