Page 349 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 349
Heuristic methods for the evaluation of environmental impacts Chapter | 12 311
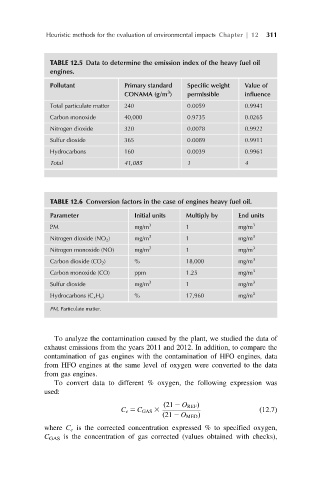
TABLE 12.5 Data to determine the emission index of the heavy fuel oil
engines.
Pollutant Primary standard Specific weight Value of
3
CONAMA (g/m ) permissible influence
Total particulate matter 240 0.0059 0.9941
Carbon monoxide 40,000 0.9735 0.0265
Nitrogen dioxide 320 0.0078 0.9922
Sulfur dioxide 365 0.0089 0.9911
Hydrocarbons 160 0.0039 0.9961
Total 41,085 1 4
TABLE 12.6 Conversion factors in the case of engines heavy fuel oil.
Parameter Initial units Multiply by End units
PM mg/m 3 1 mg/m 3
Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) mg/m 3 1 mg/m 3
Nitrogen monoxide (NO) mg/m 3 1 mg/m 3
Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) % 18,000 mg/m 3
Carbon monoxide (CO) ppm 1.25 mg/m 3
Sulfur dioxide mg/m 3 1 mg/m 3
Hydrocarbons (C x H y ) % 17,960 mg/m 3
PM, Particulate matter.
To analyze the contamination caused by the plant, we studied the data of
exhaust emissions from the years 2011 and 2012. In addition, to compare the
contamination of gas engines with the contamination of HFO engines, data
from HFO engines at the same level of oxygen were converted to the data
from gas engines.
To convert data to different % oxygen, the following expression was
used:
ð 21 2 O REF Þ
C c 5 C GAS 3 ð12:7Þ
ð 21 2 O MED Þ
where C c is the corrected concentration expressed % to specified oxygen,
C GAS is the concentration of gas corrected (values obtained with checks),