Page 352 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 352
314 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
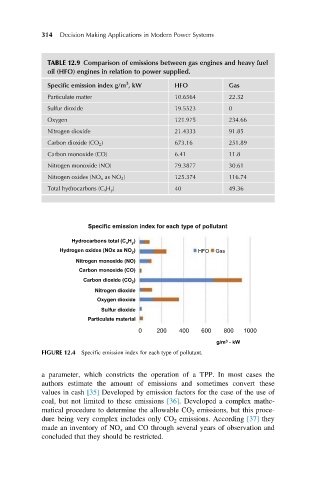
TABLE 12.9 Comparison of emissions between gas engines and heavy fuel
oil (HFO) engines in relation to power supplied.
3
Specific emission index g/m , kW HFO Gas
Particulate matter 10.6564 22.32
Sulfur dioxide 19.5523 0
Oxygen 121.975 234.66
Nitrogen dioxide 21.4333 91.85
Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) 673.16 251.89
Carbon monoxide (CO) 6.41 11.8
Nitrogen monoxide (NO) 79.3877 30.61
Nitrogen oxides (NO x as NO 2 ) 125.374 116.74
Total hydrocarbons (C x H y ) 40 49.36
Specific emission index for each type of pollutant
Hydrocarbons total (C H )
y
x
Hydrogen oxides (NOx as NO ) HFO Gas
2
Nitrogen monoxide (NO)
Carbon monoxide (CO)
)
Carbon dioxide (CO 2
Nitrogen dioxide
Oxygen dioxide
Sulfur dioxide
Particulate material
0 200 400 600 800 1000
3
g/m - kW
FIGURE 12.4 Specific emission index for each type of pollutant.
a parameter, which constricts the operation of a TPP. In most cases the
authors estimate the amount of emissions and sometimes convert these
values in cash [35] Developed by emission factors for the case of the use of
coal, but not limited to these emissions [36]. Developed a complex mathe-
matical procedure to determine the allowable CO 2 emissions, but this proce-
dure being very complex includes only CO 2 emissions. According [37] they
made an inventory of NO x and CO through several years of observation and
concluded that they should be restricted.