Page 466 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 466
Multistage and decentralized operations of Chapter | 16 425
An auxiliary binary decision variable, that is, b c tðÞ, is utilized to model
the consecutive participation constraint. b c tðÞ 5 1 indicates the beginning of a
new block of consecutive participation at t. Eqs. (16.31) (16.35) guarantee
that the number of consecutive participating time steps is greater or equal to
N c . Incorporating binary decision variables into the optimization problems
results in a mixed-integer programming problem, where sophisticated numer-
ical solvers are needed. With PDR market integration the overall problem is
formulated as follows:
Problem 4—TOU charges with PDR market participation
Objective minimizeC EC 1 C DC 2 R PDR
Subject to (16.1) (16.9) and (16.26) (16.35)
16.4 Cost-saving performance in different markets
Results of optimizations of EVs in DR programs and ancillary service markets
described earlier are presented here. The first example optimizes charging sche-
dules solely to minimize electric TOU costs. The second example optimizes to
minimize TOU costs and maximize ancillary service regulation revenue.
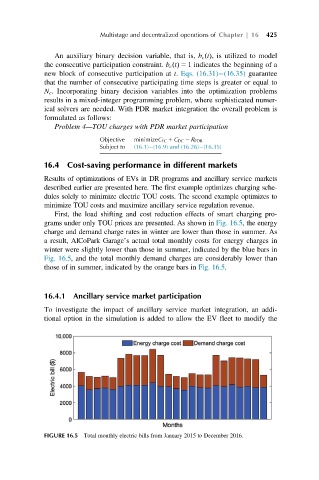
First, the load shifting and cost reduction effects of smart charging pro-
grams under only TOU prices are presented. As shown in Fig. 16.5, the energy
charge and demand charge rates in winter are lower than those in summer. As
a result, AlCoPark Garage’s actual total monthly costs for energy charges in
winter were slightly lower than those in summer, indicated by the blue bars in
Fig. 16.5, and the total monthly demand charges are considerably lower than
those of in summer, indicated by the orange bars in Fig. 16.5.
16.4.1 Ancillary service market participation
To investigate the impact of ancillary service market integration, an addi-
tional option in the simulation is added to allow the EV fleet to modify the
FIGURE 16.5 Total monthly electric bills from January 2015 to December 2016.