Page 485 - Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures
P. 485
SHEAR WALLS 7.47
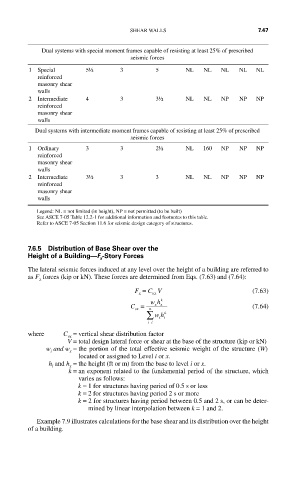
Dual systems with special moment frames capable of resisting at least 25% of prescribed
seismic forces
1 Special 5½ 3 5 NL NL NL NL NL
reinforced
masonry shear
walls
2 Intermediate 4 3 3½ NL NL NP NP NP
reinforced
masonry shear
walls
Dual systems with intermediate moment frames capable of resisting at least 25% of prescribed
seismic forces
1 Ordinary 3 3 2½ NL 160 NP NP NP
reinforced
masonry shear
walls
2 Intermediate 3½ 3 3 NL NL NP NP NP
reinforced
masonry shear
walls
Legend: NL = not limited (in height), NP = not permitted (to be built)
See ASCE 7-05 Table 12.2-1 for additional information and footnotes to this table.
Refer to ASCE 7-05 Section 11.6 for seismic design category of structures.
7.6.5 Distribution of Base Shear over the
Height of a Building—F -Story Forces
x
The lateral seismic forces induced at any level over the height of a building are referred to
as F forces (kip or kN). These forces are determined from Eqs. (7.63) and (7.64):
x
F = C V (7.63)
x vx
C = wh k (7.64)
xx
vx n
∑ wh k
ii
ii =
where C = vertical shear distribution factor
vx
V = total design lateral force or shear at the base of the structure (kip or kN)
w and w = the portion of the total effective seismic weight of the structure (W)
i
x
located or assigned to Level i or x.
h and h = the height (ft or m) from the base to level i or x.
i
x
k = an exponent related to the fundamental period of the structure, which
varies as follows:
k = 1 for structures having period of 0.5 s or less
k = 2 for structures having period 2 s or more
k = 2 for structures having period between 0.5 and 2 s, or can be deter-
mined by linear interpolation between k = 1 and 2.
Example 7.9 illustrates calculations for the base shear and its distribution over the height
of a building.