Page 150 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 150
3.2 HELIOSTAT FIELD EFFICIENCY ANALYSIS 135
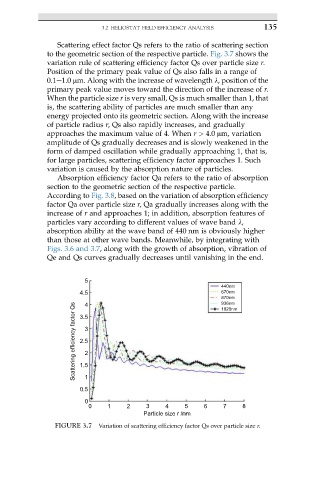
Scattering effect factor Qs refers to the ratio of scattering section
to the geometric section of the respective particle. Fig. 3.7 shows the
variation rule of scattering efficiency factor Qs over particle size r.
Position of the primary peak value of Qs also falls in a range of
0.1e1.0 mm. Along with the increase of wavelength l, position of the
primary peak value moves toward the direction of the increase of r.
When the particle size r is very small, Qs is much smaller than 1, that
is, the scattering ability of particles are much smaller than any
energy projected onto its geometric section. Along with the increase
of particle radius r, Qs also rapidly increases, and gradually
approaches the maximum value of 4. When r > 4.0 mm, variation
amplitude of Qs gradually decreases and is slowly weakened in the
form of damped oscillation while gradually approaching 1, that is,
for large particles, scattering efficiency factor approaches 1. Such
variation is caused by the absorption nature of particles.
Absorption efficiency factor Qa refers to the ratio of absorption
section to the geometric section of the respective particle.
According to Fig. 3.8, based on the variation of absorption efficiency
factor Qa over particle size r, Qa gradually increases along with the
increase of r and approaches 1; in addition, absorption features of
particles vary according to different values of wave band l,
absorption ability at the wave band of 440 nm is obviously higher
than those at other wave bands. Meanwhile, by integrating with
Figs. 3.6 and 3.7, along with the growth of absorption, vibration of
Qe and Qs curves gradually decreases until vanishing in the end.
5
440nm
4.5 670nm
870nm
936nm
4
Scattering efficiency factor Qs 2.5 3 2
1020nm
3.5
1.5
0.5 1
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Particle size r /mm
FIGURE 3.7 Variation of scattering efficiency factor Qs over particle size r.